-
-
A Geotechnical Review of the Status and Causes of Overtopping Damage to an Earth Fill Dam
필댐 월류피해 및 원인에 대한 지반공학적 관점의 고찰
-
Chan Yu
유찬
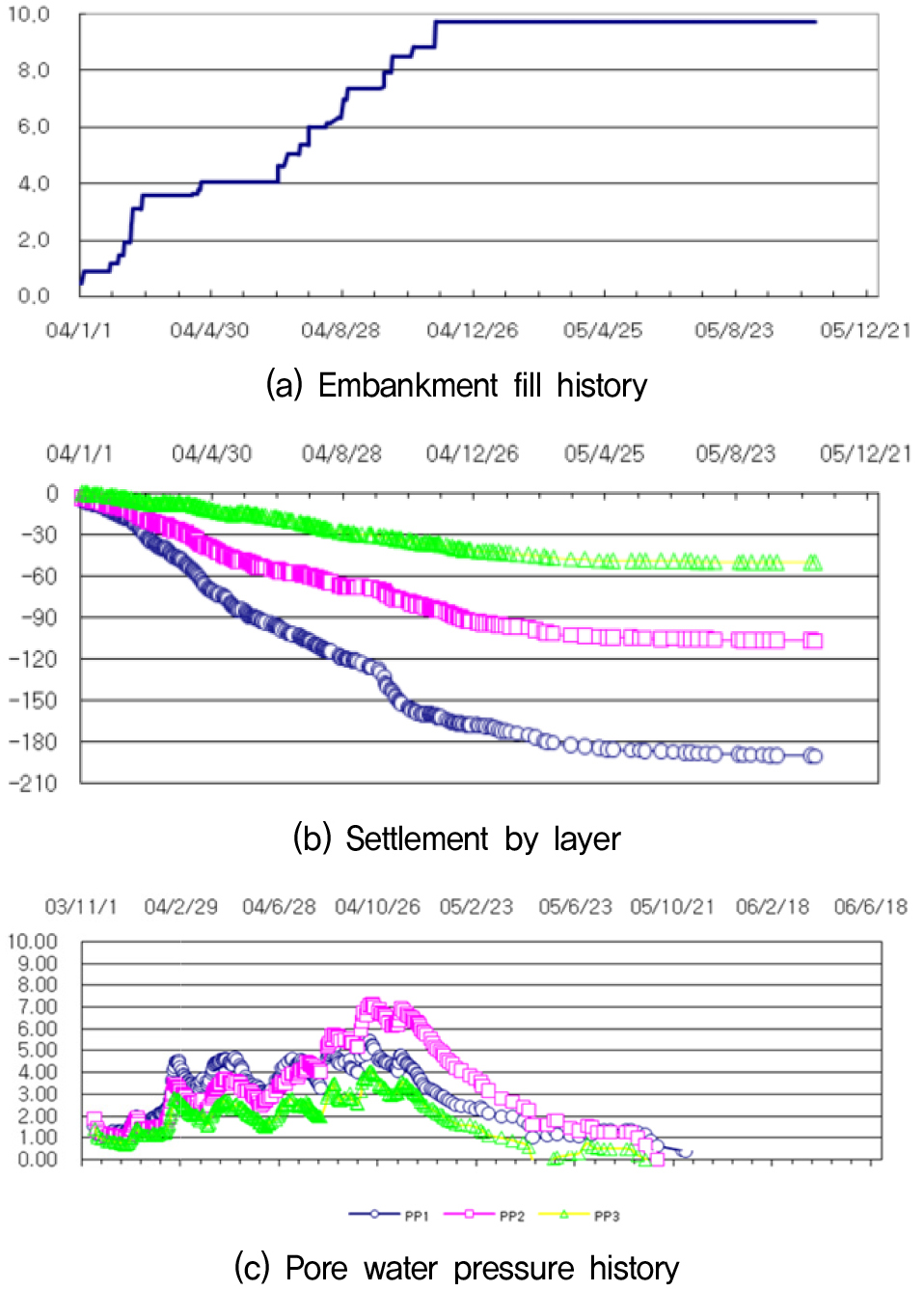
- This paper presents a field investigation, data collection, and analysis of an overtopping event at a medium-sized agricultural earth fill dam (completed …
실제 흙댐 월류발생 사례에 대해서 현장 조사, 자료 수집 및 분석을 실시하였다. 대상 흙댐은 중형의 농업용 저수지로서 1975년에 준공되어 대략 50년 동안 …
- This paper presents a field investigation, data collection, and analysis of an overtopping event at a medium-sized agricultural earth fill dam (completed in 1975) that experienced overflow during a typhoon in September 2023. The overflow caused downstream slope erosion around the embankment core and prompted evacuation warnings for downstream residents. Ongoing rainfall and concerns about further embankment collapse limited the opportunity for detailed geotechnical testing during emergency repairs. Therefore, this study analyzed on-site visual and photographic records and dam water-level measurements taken immediately after the overflow, along with existing research data documenting pre- and postevent conditions. Results suggest that the combined effects of downstream slope vegetation, grouting reinforcement within the embankment during repair, overflow velocity, and overflow duration likely contributed to preventing catastrophic failure under the emergency overflow. However, limited information prevented quantification of each factor’s contribution. The findings underscore that deficiencies in any single design or maintenance element could produce more severe damage and highlight the importance of faithful implementation of design, construction, and maintenance practices to mitigate overtopping risk.
- COLLAPSE
실제 흙댐 월류발생 사례에 대해서 현장 조사, 자료 수집 및 분석을 실시하였다. 대상 흙댐은 중형의 농업용 저수지로서 1975년에 준공되어 대략 50년 동안 운영되어 왔으며, 2023년 9월 태풍의 영향으로 월류가 발생되어 하류 주민들에 대한 대피명령이 내려졌고, 제체 하류사면이 코어층 깊이까지 침식이 진행되었다. 그러나 계속되는 강우와 추가적인 제체 붕괴의 우려로 손상된 하류 사면은 신속하게 복구해야 했고, 이로 인하여 정확한 지반공학적 조사와 시험이 불가능 했다. 따라서 본 논문에서는 사고발생 직후 참여한 현장 육안조사 및 영상자료 그리고 저수위 계측자료를 분석하여 월류발생 전후 상황에서 제체의 침식발생과 붕괴 직전까지 상황을 기존 연구 자료들과 비교/분석한 내용을 정리하였다. 연구결과 하류사면 보호 식생, 보수공사기간에 이루어진 제체 내 그라우팅 보강, 월류 속도, 그리고 월류지속 시간의 복합적인 영향이 긴급 월류 상황에서도 제체의 완전 붕괴가 발생하지 않은 데 기여했을 것으로 추정된다. 그러나 정보 부족으로 인해 각각의 단일 요소의 영향을 정량화하는 데에는 한계가 있었다. 이 결과는 기존의 댐 설계의 각 요소 중 하나라도 부족했다면 더 심각한 피해가 발생했을 가능성을 시사한다. 또한 언급된 다양한 요소들이 설계 및 시공에 충실히 반영 및 시공되었고, 지속적인 유지관리와 보수보강이 사고 피해를 최소화하였을 것으로 추정된다.
-
A Geotechnical Review of the Status and Causes of Overtopping Damage to an Earth Fill Dam
-
-
Site Classification-Based Shear Wave Velocity Distribution and Depth-Dependent COV Models for Soils for Seismic Design
내진설계를 위한 지반분류별 전단파속도 분포 특성 및 깊이에 따른 전단파속도의 변동계수 모델식 제안
-
Hyun-Ju Oh, Du-San Bae, Hyung-Choon Park
오현주, 배두산, 박형춘
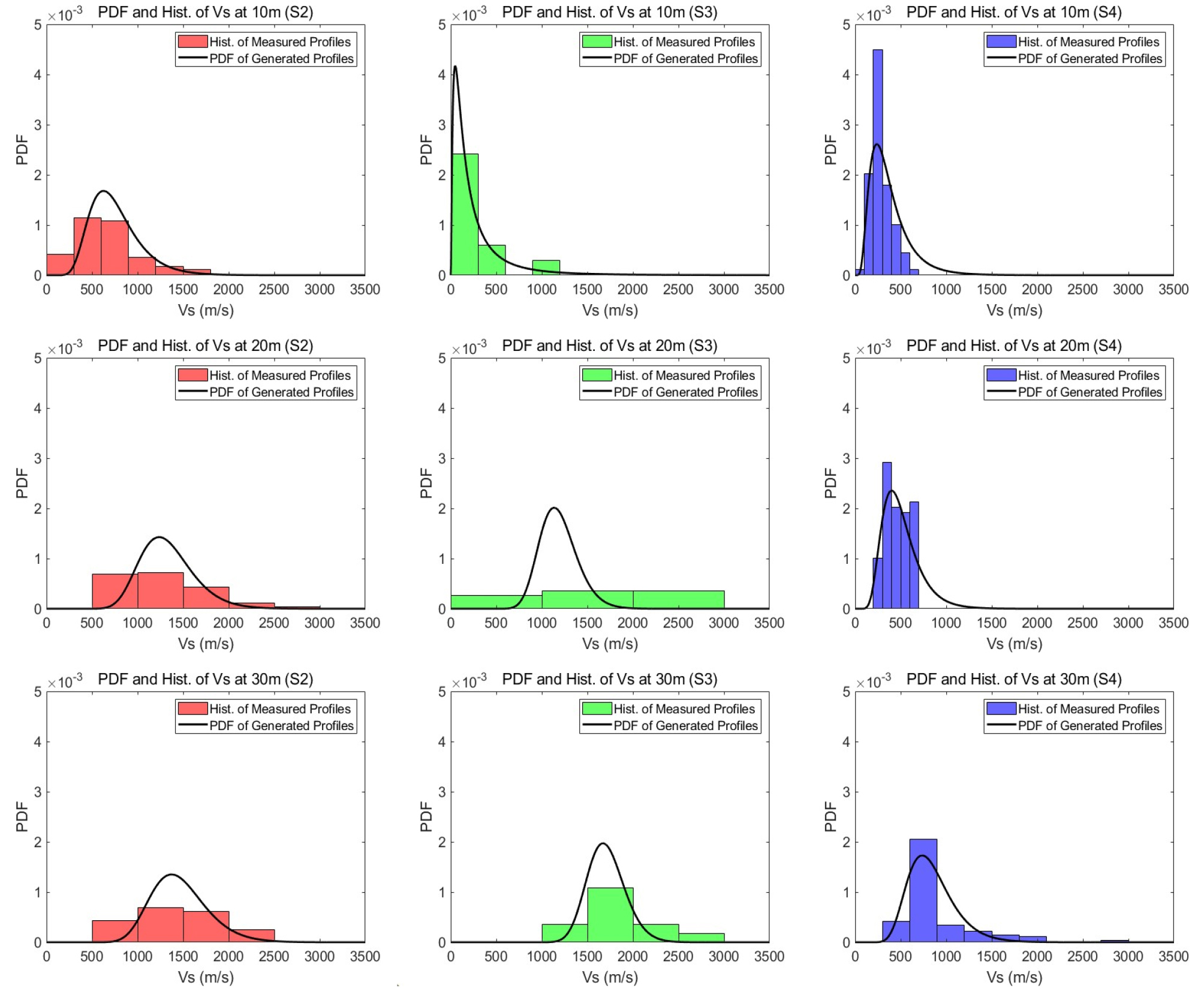
- Soil shear wave velocity (Vs) profiles govern seismic wave amplification and attenuation and thus strongly influence seismic design. Due to time and …
지반의 전단파속도(Vs) 주상도는 내진설계에 있어 지진파의 증·감폭 특성을 결정짓는 핵심 요소이다. 그러나 시간·경제적 제약으로 인해 충분한 수의 지반조사를 수행하기 어려워, 실무에서는 제한된 …
- Soil shear wave velocity (Vs) profiles govern seismic wave amplification and attenuation and thus strongly influence seismic design. Due to time and cost constraints, practitioners often use the average of a limited number of Vs profiles, which neglects spatial variability. This uncertainty can be addressed using reliability-based probabilistic analysis that generates random Vs fields via statistical methods and applies Monte Carlo simulation or coefficient of variation (COV)-based evaluation. Using 160 downhole test datasets from site development in Sejong City, sites were classified by the average Vs of the upper soil layer (Vs, soil). The sites were classified into three soil profile types: S2 (55 cases), S3 (16 cases), and S4 (89 cases). For each class, 243 (S2), 193 (S3), and 243 (S4) possible Vs profiles were generated. The distribution characteristics of Vs were assessed for each soil classification, and depth-dependent COV models applicable to reliability-based seismic analyses are proposed.
- COLLAPSE
지반의 전단파속도(Vs) 주상도는 내진설계에 있어 지진파의 증·감폭 특성을 결정짓는 핵심 요소이다. 그러나 시간·경제적 제약으로 인해 충분한 수의 지반조사를 수행하기 어려워, 실무에서는 제한된 횟수의 조사를 통해 얻은 전단파속도 주상도의 평균을 대표값으로 사용하게 된다. 이는 지반 물성치의 공간적 변동성을 고려하지 못해, 지진 시 실제 지반 거동과 해석 결과 사이에 차이를 유발할 수 있다. 이러한 불확실성은 확률론 기반의 신뢰성 해석을 통해 반영할 수 있으며, 통계적 방법을 활용해 전단파속도 랜덤 필드를 생성하고, 이를 바탕으로 몬테카를로 시뮬레이션이나 변동계수(COV)를 활용한 해석을 수행할 수 있다. 본 연구에서는 세종특별자치시 부지조성 단계에서 수행된 160개의 다운홀 시험 데이터를 활용하여, 토층 평균 전단파속도(Vs,soil)를 기준으로 S2 지반(55개), S3 지반(16개), S4 지반(89개)으로 분류하였다. 이후 각각에 대해 존재 가능한 전단파속도 주상도 243개(S2), 193개(S3), 243개(S4)를 생성하였으며, 이를 바탕으로 지반분류별 전단파속도 분포 특성을 평가하고, 깊이-전단파 속도 모델식을 제안하였으며, 신뢰성 기반 해석에 활용 가능한 깊이별 전단파속도 변동계수 모델식을 제안하였다.
-
Site Classification-Based Shear Wave Velocity Distribution and Depth-Dependent COV Models for Soils for Seismic Design
-

-
Propagation Characteristics of Blasting Noise and Noise Impact Assessment for Nonelectric Detonator Blasting in Tunnel Portals
터널갱구부 비전기 뇌관발파시 발파소음의 전파특성 및 영향평가 방법
-
Jin-Wook Oh, Yu-Seok Shin, Kang-Il Lee
오진욱, 신유석, 이강일
- As tunnel construction in urban areas increases, reducing blasting noise has become critical. Selection of effective soundproof systems for tunnel portals is …
최근 들어 철도노선의 연장, 광역급행철도 신설 등으로 도심지의 터널시공을 위한 발파가 빈번해짐에 따라 발파소음수준의 저감을 위한 연구도 활발하게 수행되어 왔다. 그러나 터널 …
- As tunnel construction in urban areas increases, reducing blasting noise has become critical. Selection of effective soundproof systems for tunnel portals is hindered by limited comparative data on noise reduction relative to distance and portal configuration. Additionally, prediction methods for blasting noise vary, producing debate over impact assessments and compliance with noise limits. To address these issues, we conducted nonelectric detonator blasting tests in three domestic tunnel portals with different soundproof systems. Results indicate that steel-frame panel soundproof walls are more effective at reducing blasting noise than a flexible soundproof door made from soft materials such as tire mats. Among prediction methods, those by Lee (2003) and EX (2009) provided better agreement with measured noise level for tunnel portals.
- COLLAPSE
최근 들어 철도노선의 연장, 광역급행철도 신설 등으로 도심지의 터널시공을 위한 발파가 빈번해짐에 따라 발파소음수준의 저감을 위한 연구도 활발하게 수행되어 왔다. 그러나 터널 입구에 발파 및 방음 시스템을 다르게 설치할 경우 발파 지점과의 거리에 따라 소음 수준 감소 효과가 달라질 수 있음에도 불구하고 이에 대한 연구 결과가 부족하여 효과적인 방음 시스템 선정에 문제가 있었다. 또한 소음영향평가 수행시 발파소음의 예측방법이 상이하기 때문에 발파소음수준 예측 및 발파소음의 소음 규제기준 초과여부 결정에 대한 논란도 지속되고 있다. 이에 본 연구에서는 이와 같은 문제를 해결하기 위해 방음시스템을 달리 설치한 국내 3개소의 터널갱구부를 대상으로 비전기식 뇌관 시험발파를 수행하였다. 연구결과, 철재 프레임과 판넬로 구성된 방음벽이 타이어매트와 같은 연성 재질로 구성된 방음문보다 발파소음의 저감에 효과적이었고, 터널갱구부에 대한 발파소음 예측은 Lee(2003)과 EX(2009)의 예측방법이 좀 더 적합한 것으로 분석되었다.
-
Propagation Characteristics of Blasting Noise and Noise Impact Assessment for Nonelectric Detonator Blasting in Tunnel Portals
-
-
Analysis of the Load-Sharing Characteristics of a Piled Raft through Field Tests
현장시험 분석을 통한 말뚝지지 전면기초의 하중분담 특성
-
Seok-Woo Hong, Young-Hoon Seo
홍석우, 서영훈
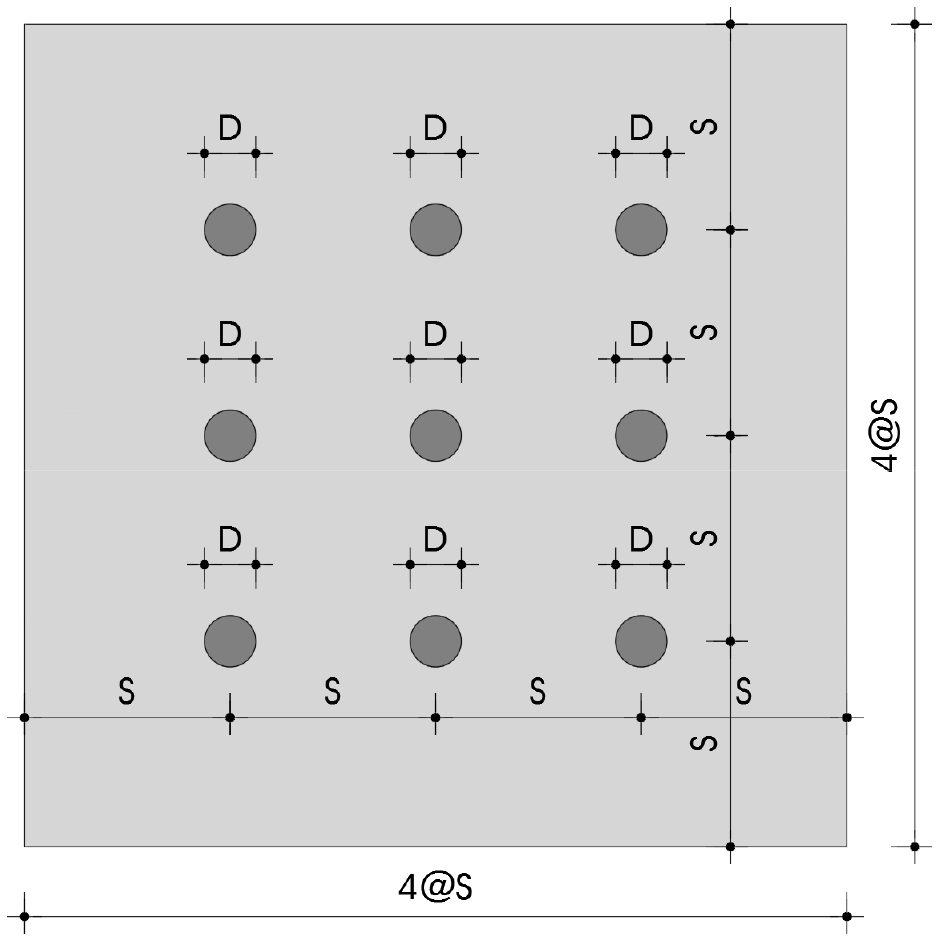
- This study explored a construction method that enhances stability and economic efficiency for future large structures. Eight types of ground strength constants …
본 연구의 출발은 앞으로 지어질 대형 구조물에 대하여 지금보다 안정성을 확보하면서도 경제성이 확보되는 기초공법에 대한 고민에서 시작되었으며, 국내 대형 구조물 현장에서 실시된 …
- This study explored a construction method that enhances stability and economic efficiency for future large structures. Eight types of ground strength constants were calculated through analytical methods. The load-sharing rate was assessed using four pile diameters and five spacing ratios based on the calculated ground strength constants. In addition, the effects of cohesion force, internal friction angle, and deformation coefficient on ground deformation under load were investigated. An individual review was conducted, confirming that the deformation coefficient is the most significant parameter affecting ground subsidence. To accurately apply the deformation coefficient, which is critical for utilizing the formula proposed in this study for practical piled raft design, we directly compared the deformation coefficient values obtained from pressuremeter tests and large-scale plate bearing tests at the site. The results revealed a significant deviation in the range of 258%–618%. Establishing a clear theory through further tests on the correlation of the deformation coefficient between the pressuremeter and large-scale plate bearing tests could enable more precise design of piled rafts using the formula proposed in this study.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구의 출발은 앞으로 지어질 대형 구조물에 대하여 지금보다 안정성을 확보하면서도 경제성이 확보되는 기초공법에 대한 고민에서 시작되었으며, 국내 대형 구조물 현장에서 실시된 대형평판재하시험을 실시한 네 곳의 자료와 유한요소해석을 통해 분석하여 8종류의 지반강도정수를 산정하였다. 산정된 지반강도정수의 조건으로 4가지 말뚝 직경과 5가지의 간격비로 하중분담률을 분석하였으며, 지반강도정수의 각 매개변수 점착력, 내부마찰각, 변형계수가 하중에 따른 지반의 변형에 미치는 영향을 파악하기 위해 개별적 검토를 실시하였으며, 검토 결과 지반의 침하에는 변형계수가 가장 큰 직접적인 매개변수임을 확인 할 수 있었다. 본 연구에서 제안한 식을 말뚝지지 전면기초의 실무 설계에 적용하기 위하여 가장 중요한 변수인 변형계수의 정확한 적용을 위해 사례 현장의 공내재하시험 변형계수 값과 대형평판재하시험 변형계수 값을 직접 비교한 결과를 정리하였으며, 그 결과가 258%~618%의 큰 편차가 있는 것으로 확인되었다. 대형평판재하시험과 공내재하시험과의 변형계수 상관관계에 대한 추가적인 시험을 통해 명확한 이론이 정립이 되면 본 연구에서 제안된 식을 이용한 말뚝지지 전면기초 설계를 보다 정확히 할 수 있을 것으로 판단된다.
-
Analysis of the Load-Sharing Characteristics of a Piled Raft through Field Tests
-
-
Bearing Characteristics and Optimal Installation Conditions of 2-row Micropiles Resisting Lateral Loads Based on Numerical Analysis
수치해석을 통한 수평하중에 저항하는 복열 마이크로파일의 지지특성 및 적정 설치조건
-
Mu-Yeun Kim, Seung-Min Hwang, Kang-Il Lee
김무연, 황승민, 이강일
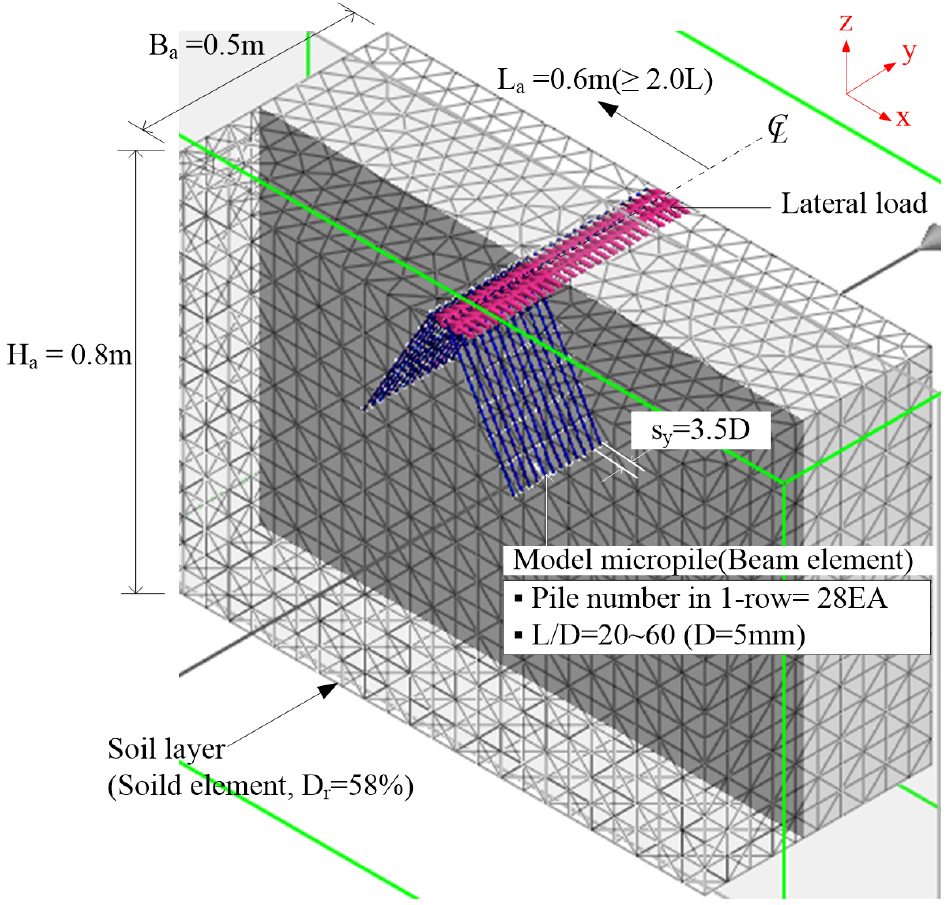
- Micropiles with diameters of 300 mm or less are commonly installed beneath existing or new structures in group configurations. Unlike conventional piles …
기존 또는 신설 구조물 기초의 하부에 설치되는 300mm 이하의 마이크로파일은 군말뚝형태로 설치된다. 그리고 이 파일은 다양한 설치조건으로 지반에 설치할 수 있고, 기존 …
- Micropiles with diameters of 300 mm or less are commonly installed beneath existing or new structures in group configurations. Unlike conventional piles such as PHC or steel piles, micropiles can be installed under various conditions, including different inclination angles, allowing them to effectively resist applied loads. Previous studies have shown that battered piles are effective in resisting lateral loads; however, micropiles designed for lateral resistance are often installed vertically. In this study, numerical analyses were conducted to evaluate the lateral bearing characteristics of 2-row micropiles under various installation conditions and to propose appropriate installation spacing and inclination angles. The results indicate that an installation spacing of at least 4.7 times the pile diameter is required. In addition, the lateral bearing capacity of 2-row micropiles increased compared with that of vertically installed micropiles when the installation angle ranged from −15° ≤ θ ≤ +30°.
- COLLAPSE
기존 또는 신설 구조물 기초의 하부에 설치되는 300mm 이하의 마이크로파일은 군말뚝형태로 설치된다. 그리고 이 파일은 다양한 설치조건으로 지반에 설치할 수 있고, 기존 파일(PHC파일, 강관 파일)과 달리 다양한 설치각도로 시공할 수 있다. 즉, 기초상부에 작용하는 하중에 마이크로파일이 효과적으로 저항하도록 다양한 설치조건으로 시공할 수 있다. 기존 연구결과를 통해 알 수 있듯이 기초상부에 수평하중이 작용하는 경우 경사파일이 효과적이다. 그럼에도 수평하중에 저항하기 위해 설치하는 마이크로파일은 기존 파일과 같이 직항으로 설치한다. 이에 본 연구에서는 다양한 설치조건 고려한 복열 마이크로파일의 수평지지특성을 평가하고 적정 설치간격과 설치각도를 제안하기 위해 수치해석을 수행하였다. 그리고 적정 설치간격은 파일직경의 4.7배 이상이고, 설치각도 -15°≤θ≤+30°인 경우 복열 마이크로파일의 수평지지력이 직항인 복열 마이크로파일보다 증가함을 연구결과를 통해 확인하였다.
-
Bearing Characteristics and Optimal Installation Conditions of 2-row Micropiles Resisting Lateral Loads Based on Numerical Analysis
-
-
Dynamic Behavior Analysis of Underground Railway Box Structures Considering Korean Ground Conditions
국내 지반조건을 반영한 철도 지하 박스 구조물의 동적 거동 분석
-
YuSeong Lee, Seokjung Kim, Mintaek Yoo
이유성, 김석중, 유민택
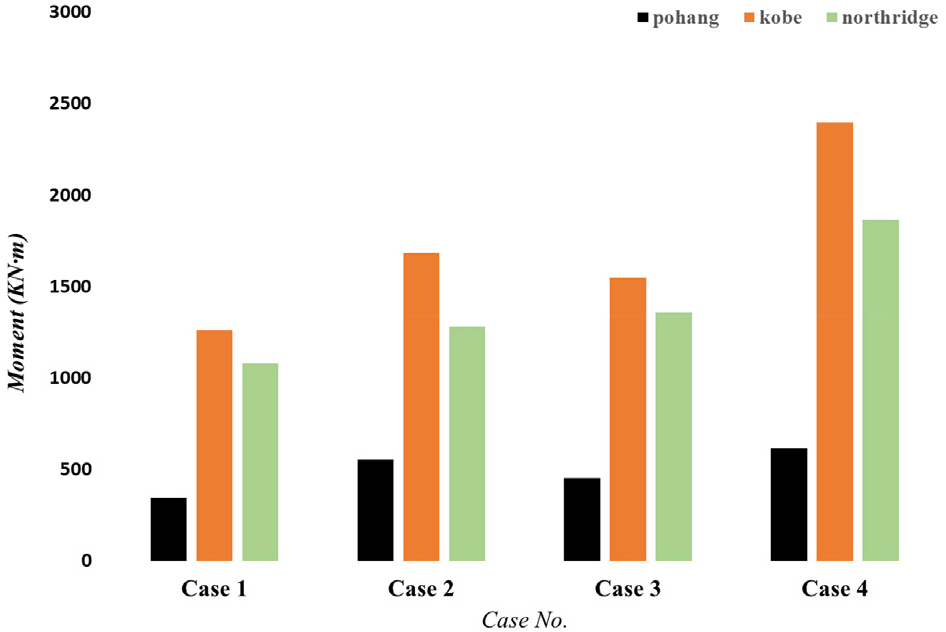
- This study developed a two-dimensional (2D) finite element model to evaluate the seismic performance of underground railway box structures under representative Korean …
본 연구는 지진 발생 시 한국의 지반 조건에 맞는 지하 철도 지하 박스 구조물의 내진 성능을 평가하기 위한 2차원 유한요소 모델을 개발하였다. …
- This study developed a two-dimensional (2D) finite element model to evaluate the seismic performance of underground railway box structures under representative Korean ground conditions. The proposed model was validated by comparing its dynamic response with results obtained from the one-dimensional (1D) site response analysis program DEEPSOIL. The structural geometry and specifications were based on a cut-and-cover station concourse in Korea. Using this model, the dynamic behavior of the structure was analyzed under varying input ground motion characteristics, tunnel embedment depths, and ground shear wave velocities. The results show that the frequency content of the input ground motion and ground stiffness strongly influence the structural response. Bending moments acting on the sidewalls and top slab increased as ground stiffness decreased and tunnel embedment depth increased.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 지진 발생 시 한국의 지반 조건에 맞는 지하 철도 지하 박스 구조물의 내진 성능을 평가하기 위한 2차원 유한요소 모델을 개발하였다. 제안된 모델은 1차원 부지응답 해석 프로그램인 DEEPSOIL을 활용하여 비선형 지반의 동적 응답을 비교 및 검증하였으며, 지하 박스 구조물의 형상 및 제원은 실제 한국의 개착식 대합실의 시설 계획을 기반으로 설정하였다. 본 모델을 통하여 입력 지진파의 특성, 지하 박스 구조물의 근입 깊이, 지반의 전단파 속도 등 다양한 변수에 따른 동적 거동 특성을 분석하였다. 그 결과, 입력 지진파의 주파수 성분과 지반의 강성에 따라 구조물의 동적 응답 특성이 상이하게 나타났으며, 지반의 강성이 낮고 지하 박스 구조물의 근입 깊이가 깊어질수록 측벽 및 상부 슬래브에 작용하는 휨 모멘트가 증가하는 경향을 보였다.
-
Dynamic Behavior Analysis of Underground Railway Box Structures Considering Korean Ground Conditions
-
-
Strength Characteristics of Small-Scale Sand Specimens Mixed with Fiber and Cement-Slurry Columns: Direct Shear Tests
직접전단시험을 통한 섬유 및 시멘트 슬러리 기둥이 혼합된 소형 모래 공시체의 강도 특성
-
Hong Duk Moon, Jong Yob Kim, Chao Wang, Hee-Young Sung, Seung-Wook Woo, Sung-Sik Park
문홍득, 김종엽, 왕차오, 성희영, 우승욱, 박성식
- Vegetation roots can increase ground mechanical stability, and many studies emulate this effect by randomly mixing fibers into soils. In this study, …
자연에는 다양한 식생이 토사 내에 뿌리를 내리고 지반의 물리적 안정성에 기여하고 있다. 대부분의 기존 연구는 섬유를 모래나 점토에 분산 혼합하는 방식을 사용하나, …
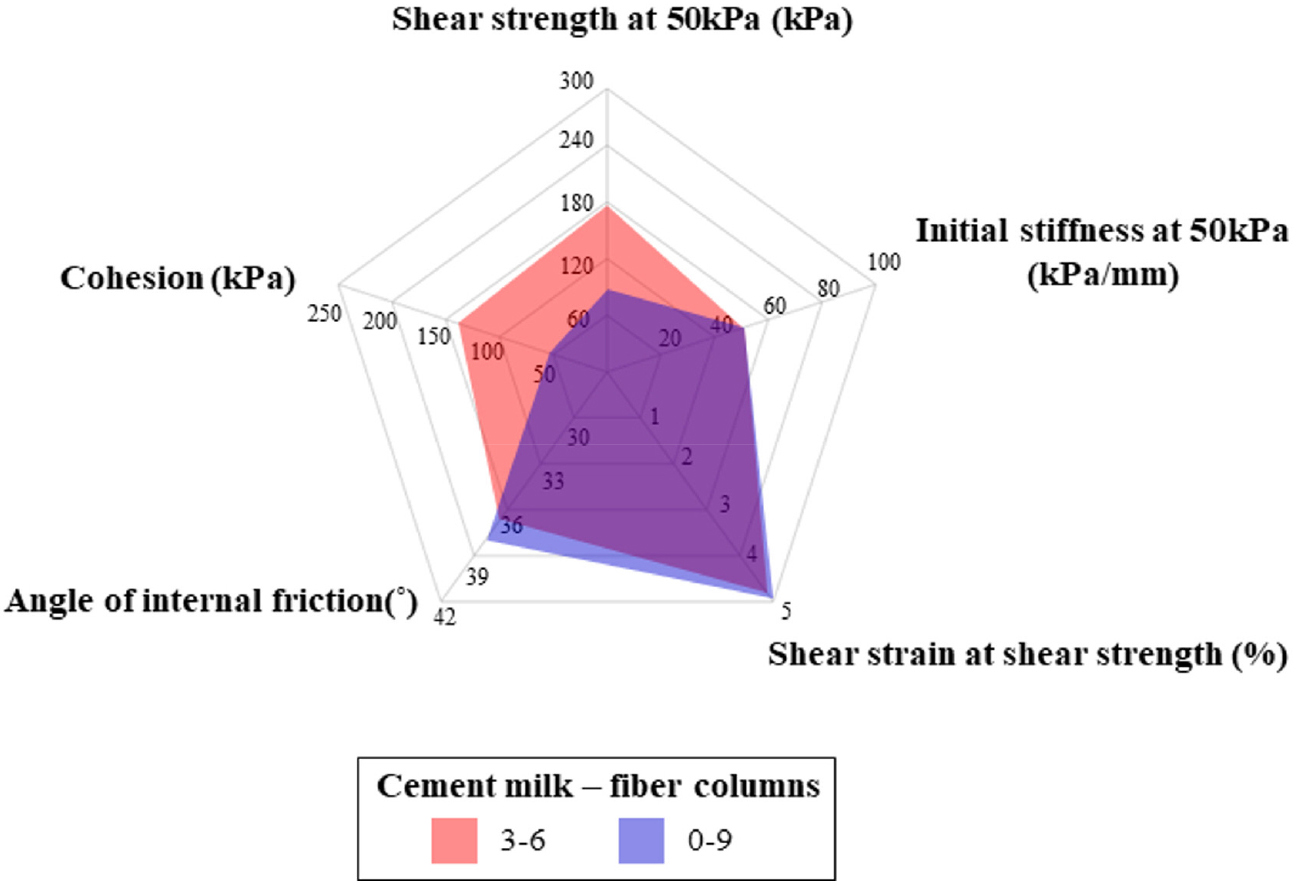
- Vegetation roots can increase ground mechanical stability, and many studies emulate this effect by randomly mixing fibers into soils. In this study, fiber bundles and cement slurry columns were embedded in uniform, columnar forms perpendicular to the shear direction rather than mixed randomly. Direct shear tests were conducted to investigate the effects of relative density, fiber content, and the distribution of cement slurry columns (having equal volume to the fiber bundles) on shear strength. The combined influence of fibers and cementation on sand shear strength was also evaluated. Results show that both fiber bundles and cement slurry columns increase peak shear strength. The internal friction angle of fiber-reinforced sand increased from 35° to 38° in loose specimens and up to 41° in dense specimens. Cohesion of sand reinforced with cement slurry increased from 0 kPa to 190 kPa in loose sand and from 11 kPa to 230 kPa in dense sand. Distributing the same fiber volume across multiple insertion points further improved shear strength. When both materials were combined, simultaneous increases in internal friction angle and cohesion were observed.
- COLLAPSE
자연에는 다양한 식생이 토사 내에 뿌리를 내리고 지반의 물리적 안정성에 기여하고 있다. 대부분의 기존 연구는 섬유를 모래나 점토에 분산 혼합하는 방식을 사용하나, 본 연구에서는 전단 방향과 직각으로 기둥 형태로 일정하게 분산 매립하였다. 가는 섬유 다발과 시멘트 슬러리 기둥과 같이 강도와 강성이 서로 다른 물질을 모래에 혼합시켜 직접전단시험을 수행하였다. 두 종류의 상대밀도와 세 종류의 섬유비 그리고 섬유 다발과 동일한 부피의 시멘트 슬러리 기둥의 분포도에 따른 전단강도 변화를 연구하였다. 또한, 섬유 다발과 시멘트 슬러리 기둥을 복합적으로 매립하여 각각의 재료가 모래의 전단강도에 미치는 영향을 분석하였다. 그 결과, 섬유 다발과 시멘트 슬러리 기둥 모두 모래의 최대전단응력을 증가시켰다. 모래의 내부마찰각은 섬유로 보강한 경우 상당히 증가하였으며, 느슨한 경우는 35°에서 38°로, 조밀한 경우는 38°에서 최대 41°까지 증가하였다. 점착력은 시멘트 슬러리로 보강한 경우 느슨한 모래는 0 kPa에서 190 kPa로, 조밀한 모래는 11 kPa에서 최대 230 kPa까지 증가하였다. 특히 동일한 섬유비에서 더 많은 지점에 나누어 매립하는 것이 모래의 전단강도를 더 증가시켰다. 그리고, 두 재료를 복합적으로 모래에 사용한 경우 각각의 특성이 모두 발현되었으며, 즉 모래의 내부마찰각과 점착력이 모두 증가하는 효과를 얻을 수 있었다.
-
Strength Characteristics of Small-Scale Sand Specimens Mixed with Fiber and Cement-Slurry Columns: Direct Shear Tests
-
-
Analysis of Failure Susceptibility due to Rainfall Infiltration Considering Vegetation Conditions on Slopes
비탈면 식생 유무에 따른 강우침투에 의한 붕괴 민감도 분석
-
Jae-Hong Kim, Hyung-Sik Yoo, Yong-Joon Choi, Tae-Wan Kim
김재홍, 유형식, 최용준, 김태완
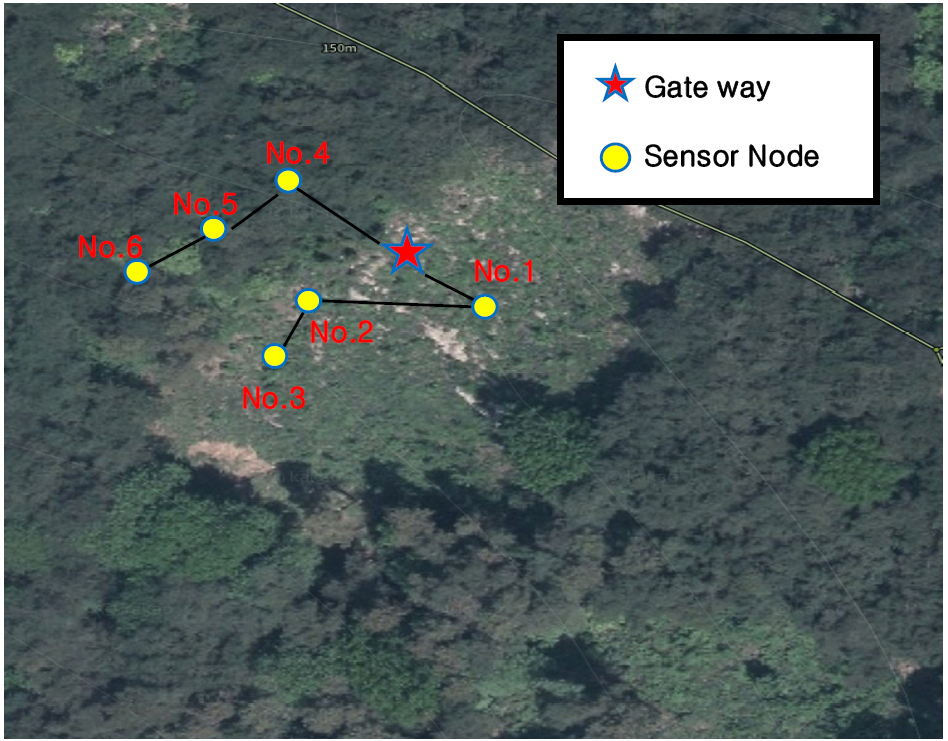
- To identify the causes of slope failures associated with logging activities, soil moisture sensors were installed in both forested and deforested areas …
산비탈에 벌목으로 인한 비탈면 붕괴가 발생하는 원인을 확인하고자 수풀지역과 벌목지역이 혼재된 사면을 대상으로 함수비 센서를 설치하여 장마철 강우량 침투를 분석하였다. 본 연구에서는 …
- To identify the causes of slope failures associated with logging activities, soil moisture sensors were installed in both forested and deforested areas to monitor rainfall infiltration during the rainy season. This study examined a method for evaluating shallow slope failure using the volumetric water content gradient (VWCG) and the Effective cumulative rainfall (ECR) under different vegetation conditions. A real-time monitoring system based on a Wireless Sensor Network was established to measure soil moisture at multiple locations, from which VWCG values were calculated. The relationship between VWCG, ECR values, and observed slope failures was then analyzed. The results show that slope failures occurred primarily in areas where both indices reached high values simultaneously. Vegetated slopes were generally characterized by VWCG values below 0.1 and ECR values below 60 mm, whereas deforested slopes were concentrated in regions where VWCG exceeded 0.2 and ECR ranged from 40 to 70 mm. Failure probability increased with increasing values of both indices. In particular, slope failures were most frequently observed under conditions of VWCG ≥ 0.3 and ECR ≥ 80 mm, which are proposed as key threshold values for early warning of shallow slope failures.
- COLLAPSE
산비탈에 벌목으로 인한 비탈면 붕괴가 발생하는 원인을 확인하고자 수풀지역과 벌목지역이 혼재된 사면을 대상으로 함수비 센서를 설치하여 장마철 강우량 침투를 분석하였다. 본 연구에서는 식생 유무에 따른 체적함수비 증가 기울기(VWCG; Volumetric Water Content Gradient)와 유효누적강우량(ECR; Effective Cumulative Rainfall)을 활용하여 표층붕괴를 판단하는 방법을 고찰하였다. 분석 절차는 다음과 같다. 먼저, 무선센서네트워크(WSN; Wireless Sensor Network) 기반 실시간 계측시스템을 구축하여 구역별 토양 수분 함량을 측정하고 이를 토대로 체적함수비 증가 기울기(VWCG)를 산정하였다. 이후 산정된 VWCG와 ECR 값을 이용하여 표층붕괴와의 상관성을 검토하였다. 분석 결과, 체적함수비 증가 기울기(VWCG)와 유효누적강우량(ECR)이 동시에 높은 구간에서 실제 붕괴가 발생하였다. 수풀지역은 주로 VWCG 0.1 이하, ECR 60 mm 이하 범위에 분포하였으며, 벌목지역은 VWCG 0.2 이상, ECR 40~70 mm 범위에 집중적으로 나타났다. VWCG와 ECR이 높을수록 붕괴 발생 가능성이 증가하였으며, 이는 식생 분포가 임계값의 변동에 직접적인 영향을 미치는 것으로 확인되었다. 특히, VWCG ≥ 0.3 및 ECR ≥ 80 mm 조건에서 붕괴 발생이 집중적으로 관찰되어 본 연구에서는 이를 표층붕괴 조기경보를 위한 주요 임계값으로 제시하였다.
-
Analysis of Failure Susceptibility due to Rainfall Infiltration Considering Vegetation Conditions on Slopes
-
-
Evaluation of Freezing Behavior of Artificial Ground Freezing System under Groundwater Flow Conditions and Determination of Critical Flow Velocity for Window Formation
지하수 흐름 조건에서의 인공동결시스템의 동결거동 평가 및 윈도우 발생에 대한 임계 유속 평가
-
Gyu-Hyun Go, Soo-Woong Yang, Gi-Eun Ko, Seok-Yoon Woo
고규현, 양수웅, 고기은, 우석윤
- Artificial ground freezing is a ground reinforcement technique widely used in urban underground excavation projects and has recently been applied more actively, …
인공동결공법은 도심지 지하 굴착 시 활용되는 연약지반 보강기법으로서 선진국을 중심으로 최근 들어 활발히 적용되고 있다. 하지만 빠른 지하수 침투 환경을 가진 지반 …
- Artificial ground freezing is a ground reinforcement technique widely used in urban underground excavation projects and has recently been applied more actively, particularly in developed countries. However, under groundwater flow conditions, heat transfer around freezing tubes is strongly influenced by seepage, which causes significant difficulties in practical application. In this study, an indoor soil freezing chamber system was developed to evaluate ground freezing behavior under controlled groundwater flow conditions. Using Python-based postprocessing, the frozen wall formation process within the ground, which is difficult to observe directly, was visualized from experimental data, and the development pattern of the frozen wall was identified. In addition, a series of experiments was conducted to determine the range of critical groundwater flow velocity that leads to the formation of “windows” around the frozen wall.
- COLLAPSE
인공동결공법은 도심지 지하 굴착 시 활용되는 연약지반 보강기법으로서 선진국을 중심으로 최근 들어 활발히 적용되고 있다. 하지만 빠른 지하수 침투 환경을 가진 지반 조건에서는 동결관 주변의 열전달이 지하수 유동에 의해 영향을 받으면서 공법 적용에 많은 어려움이 초래된다. 본 연구에서는 빠른 지하수 흐름 조건에서의 지반 동결 거동을 평가하기 위해 실내 모형토조시스템을 자체 개발하였고, 다양한 지하수 유속 별 지반 동결 실험을 수행하였다. 토조실험을 통해 얻어진 데이터를 Python 기반의 후처리 기법을 통해 육안 관찰이 어려운 지반 내부의 동결 벽체 형성 과정을 시각화하고, 동결벽체의 양상을 확인하였다. 또한, 동결 벽체 주변 윈도우 발생을 유발하는 임계 지하수 유속의 범위를 제시하였다.
-
Evaluation of Freezing Behavior of Artificial Ground Freezing System under Groundwater Flow Conditions and Determination of Critical Flow Velocity for Window Formation
-

-
Experimental Assessment of System Configuration Effects on Size Enhancement of Microwave-Sintered Blocks
마이크로파 소결 블록 크기 향상을 위한 시스템 구성 영향 평가
-
Hyunwoo Jin, Young-Jae Kim, Jangguen Lee
진현우, 김영재, 이장근
- Interest in lunar in-situ resource utilization (ISRU) has grown with discoveries of potential resources such as water ice and He-3 on the …
달 표면에서 얼음 형태의 물, 헬륨-3과 같은 에너지자원이 발견됨에 따라 달은 심우주 탐사를 위한 전초기지로 주목받고 있다. 지속 가능한 심우주 탐사를 위해 …
- Interest in lunar in-situ resource utilization (ISRU) has grown with discoveries of potential resources such as water ice and He-3 on the Moon. Technologies that solidify lunar regolith are thus crucial for sustainable deep-space missions. Building on previous work, this study produced sintered blocks (~200 mm × 200 mm × 60 mm) using a 9 kW microwave sintering furnace and evaluated how system configuration (microwave output and location, placement of silicon carbide susceptor pieces) and sintering temperature affect block uniformity. A homogeneous sintered block was achieved at a microwave output of 2.1 kW, with susceptor pieces placed on both sides and a sintering temperature of 1,050°C. Physical and mechanical testing of cored samples indicated that the region on the backside of the microwave output location exhibited lower sintering efficiency than other positions.
- COLLAPSE
달 표면에서 얼음 형태의 물, 헬륨-3과 같은 에너지자원이 발견됨에 따라 달은 심우주 탐사를 위한 전초기지로 주목받고 있다. 지속 가능한 심우주 탐사를 위해 현지자원 활용 개념이 주목받음에 따라, 현지재료인 월면토 고형화 기술의 활용 가능성이 증대되고 있다. 본 연구에서는 기존에 선행된 기초연구들에서 얻어진 결과를 토대로 9 kW 급 마이크로파 소결로를 활용해 가로, 세로, 높이가 각각 약 200 mm, 200 mm, 60 mm인 소결 블록을 제작하였다. 이 과정에서 마이크로파 출력량 및 출력 위치, 추가 보조가열재 조각 배치 등의 소결 시스템 구성을 비롯해 소결온도가 균질한 마이크로파 소결 블록 제작에 미치는 영향을 평가하였다. 그 결과 마이크로파 출력 위치와 관계없이 2.1 kW의 출력, 양 측면 보조가열재 조각 배치, 소결온도 1,050°C에서 균질한 소결 블록이 제작되었다. 그러나 코어링된 시편에서 측정된 물리적 및 역학적 특성을 분석한 결과 마이크로파 출력 위치가 후면인 경우 다른 위치에서 출력된 것보다 상대적으로 소결 효율이 낮은 것으로 나타났다.
-
Experimental Assessment of System Configuration Effects on Size Enhancement of Microwave-Sintered Blocks
-
-
A Comparative Study on IW and Annealing-Based Coordinate Prediction Methods Using Small-Scale Geotechnical Property Data
소규모 지반 물성 자료를 활용한 IW 및 어닐링 기반 좌표 예측 기법의 비교 연구
-
Hyung-Koo Yoon
윤형구
- The kriging method, which is widely used to estimate data at unmeasured locations in geotechnical investigations, exhibits a notable limitation because its …
지반의 미측정 지점의 데이터를 유추할 수 있는 크리깅 기법은 관측 지점 간 거리가 멀어질수록 상관성이 급격히 감소하여 신뢰성이 낮은 한계를 보인다. 본 …
- The kriging method, which is widely used to estimate data at unmeasured locations in geotechnical investigations, exhibits a notable limitation because its reliability significantly decreases as the spatial correlation between observation points diminishes with distance. The objective of this study was to enhance the spatial prediction accuracy of soil depth within a small-scale geotechnical dataset by performing coordinate prediction based on Independent Weighted (IW) and Annealing algorithms. A total of 23 soil depth measurements were collected through the Dynamic Cone Penetration Test, and data sparsity was addressed using the synthetic minority over-sampling technique and adaptive synthetic sampling. The IW algorithm calculates soil depth at each grid point using a distance-weighted average for the initial prediction, while the Annealing algorithm takes the IW results as an initial solution and iteratively performs probabilistic swap operations to minimize overall error. Comparative analysis shows that after applying Annealing, the prediction error (RMSE) decreased by approximately 25–30%, and the normalized error sum (Energy) decreased by more than 40% compared to IW. Furthermore, six performance evaluation metrics were applied, all demonstrating improved reliability following the application of Annealing. These findings confirm that the proposed IW and Annealing methods provide an efficient and reliable approach for realistically reproducing soil depth distributions, even in small-scale geotechnical investigation environments.
- COLLAPSE
지반의 미측정 지점의 데이터를 유추할 수 있는 크리깅 기법은 관측 지점 간 거리가 멀어질수록 상관성이 급격히 감소하여 신뢰성이 낮은 한계를 보인다. 본 연구의 목적은 소규모 지반조사 데이터인 토심을 이용하여 공간적 예측 정확도를 향상시키기 위한 Independent Weighted(IW) 및 어닐링(Annealing) 기반으로 좌표 예측을 수행하는 것이다. Dynamic Cone Penetration Test(DCPT)를 통해 총 23개 지점에서 실측된 토심 데이터를 활용하였으며, 데이터의 희소성을 보완하기 위해 Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique(SMOTE)와 Adaptive Synthetic Sampling(ADASYN) 알고리즘을 적용하였다. IW는 각 격자점의 토심을 거리 가중 평균으로 계산하여 초기 예측을 수행하였고, 어닐링은 IW 결과를 초기 해로 설정한 후 확률적 스왑 연산을 반복 수행하여 전체 오차를 최소화하였다. 비교 결과, 어닐링 적용 후 예측 오차(RMSE)는 IW 대비 약 25~30% 감소, 정규화된 오차합(Energy)은 약 40% 이상 감소하였다. 또한 성능을 평가할 수 있는 6가지 지표 값도 제시하였으며, 모두 신뢰성이 향상된 결과를 보여줬다. 해당 연구에서 사용한 방법인 IW 및 Annealing 기법은 소규모 지반조사 환경에서도 토심 분포를 현실적으로 재현할 수 있는 효율적이고 신뢰성 높은 예측 방법임이 검증되었다.
-
A Comparative Study on IW and Annealing-Based Coordinate Prediction Methods Using Small-Scale Geotechnical Property Data
-
-
Urban Seismic Interferometry Enhanced by In-line Source Selection Using MUSIC Beamforming
도심지 교차상관 탄성파 간섭법 적용을 위한 MUSIC 빔포밍 기반 인라인 소스 선택 기법 연구
-
Seon-Ho Hwang, Chang-Ho Shin, Taeseo Ku
황선호, 신창호, 구태서
- Urban traffic noise is highly heterogeneous and nonstationary, which causes conventional stacking-based cross-correlation seismic interferometry to introduce discontinuities and bias into the …
도심 교통잡음(상시미동)은 불균등성과 비정상성이 강해, 이를 단순 적층(stacking)에 기반한 교차상관 탄성파 간섭법에 적용할 경우 주파수-위상속도 스펙트럼(Frequency - phase velocity spectrum)의 불연속과 편향을 …
- Urban traffic noise is highly heterogeneous and nonstationary, which causes conventional stacking-based cross-correlation seismic interferometry to introduce discontinuities and bias into the frequency–phase velocity spectrum. We propose a methodological framework that estimates frequency-dependent directions of arrival using Multiple Signal Classification (MUSIC) beamforming, selects the in-line sector aligned with the array axis, and reconstructs a directionally filtered wavefield via the inverse short-time Fourier transform. Using field data from Sori Park in Seoul, we compared the proposed method with multichannel analysis of surface waves (MASW) and conventional cross-correlation seismic interferometry. The proposed approach eliminated dispersion-curve discontinuities and yielded the most accurate estimates of bedrock depth (14.4 m) and bedrock velocity (1,302 m/s). By contrast, MASW (15.6 m, 783 m/s) and conventional cross-correlation seismic interferometry (11.2 m, 1,371 m/s) produced larger depth errors or underestimated velocity. These field results indicate enhanced low-frequency recoverability and improved azimuthal coherence, demonstrating that MUSIC-based in-line source selection can substantially enhance the accuracy of bedrock detection urban environments.
- COLLAPSE
도심 교통잡음(상시미동)은 불균등성과 비정상성이 강해, 이를 단순 적층(stacking)에 기반한 교차상관 탄성파 간섭법에 적용할 경우 주파수-위상속도 스펙트럼(Frequency - phase velocity spectrum)의 불연속과 편향을 유발한다. 본 연구는 Multiple Signal Classification(MUSIC) 빔포밍을 이용해 주파수별 도래각(Direction of arrival, DOA)을 추정하고, 배열축과 정렬된(in-line) 섹터만 선택한 뒤 역 단시간 푸리에 변환(Inverse Short-Time Fourier Transform, ISTFT)으로 방향성 필터링 파동장을 재구성하는 개념적 절차를 제안한다. 서울 소리공원에서 제안 기법, MASW, 기존 교차상관 탄성파 간섭법을 비교한 결과, 제안 기법이 분산곡선의 불연속성을 해결하고 역산된 기반암 심도(14.4 m) 및 속도(1,302 m/s) 추정에서 가장 높은 정확도를 보였다. 반면 MASW(15.6 m, 783 m/s)와 기존 교차상관 탄성파 간섭법(11.2 m, 1,371 m/s)은 기반암 심도 예측 오차가 크거나 속도를 과소평가하였다. 이는 현장 적용 결과, 저주파 재현성과 방위의 일관성이 향상되어 MUSIC 기반 인라인 소스선택이 도심 환경 기반암 탐지 정확도를 크게 향상시킴을 입증한다.
-
Urban Seismic Interferometry Enhanced by In-line Source Selection Using MUSIC Beamforming
-
-
Comparison of Ground Response Characteristics of Liquefiable Soils in the Pohang Area Using 1D and 2D Numerical Analyses
1D 및 2D 수치해석을 통한 포항 지역 액상화 가능 지반의 지반응답 특성 비교
-
Jun-Seong Moon, Jin-Man Kim, Su-Won Son, Jong-Chan Yoon, Yun-Ho Park, Jeong-Won Seo
문준성, 김진만, 손수원, 윤종찬, 박윤호, 서정원
- This study performed one-dimensional (1D) and two-dimensional (2D) ground response analyses for liquefaction-affected sites in the Pohang area using SHAKE2000, DEEPSOIL, and …
본 연구에서는 2017년 포항지진 피해지역을 대상으로 SHAKE2000, DEEPSOIL, PLAXIS 2D를 이용한 1차원 및 2차원 지반응답해석을 수행하였다. 동일한 입력 조건하에서 반복전단응력비(CSR), 반복저항응력비(CRR), 및 …
- This study performed one-dimensional (1D) and two-dimensional (2D) ground response analyses for liquefaction-affected sites in the Pohang area using SHAKE2000, DEEPSOIL, and PLAXIS 2D. Cyclic stress ratio (CSR), cyclic resistance ratio (CRR), and liquefaction safety factor (FS = CRR/CSR) were calculated and compared to evaluate differences among the analysis methods. SHAKE2000, which is based on an equivalent linear approach, produced the most conservative results. DEEPSOIL, using a nonlinear hysteretic model, generally yielded less conservative estimates. In contrast, PLAXIS 2D realistically reproduced liquefaction behavior by directly considering undrained response and confinement-dependent stress changes. A comparison between SPT-based and Vs-based CRR evaluations showed that the Vs-based approach exhibited better agreement with observed damage patterns, indicating its suitability for liquefaction assessment in mixed sandy soils.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구에서는 2017년 포항지진 피해지역을 대상으로 SHAKE2000, DEEPSOIL, PLAXIS 2D를 이용한 1차원 및 2차원 지반응답해석을 수행하였다. 동일한 입력 조건하에서 반복전단응력비(CSR), 반복저항응력비(CRR), 및 액상화 안전율(FS = CRR/CSR)을 산정하여 해석기법별 차이를 비교·분석하였다. SHAKE2000은 등가선형 해석으로 가장 보수적인 결과를, DEEPSOIL은 비선형 이력모델을 통해 비보수적인 경향을 보였다. 반면 PLAXIS 2D는 비배수 거동과 구속압 변화를 직접 고려하여 가장 현실적인 액상화 거동을 재현하였다. 또한 SPT 및 Vs 기반 CRR 산정 결과를 비교한 결과, Vs 기반 평가는 실제 피해구간과의 부합도가 높아 복합 사질토 지반의 액상화 평가에 더 적합한 것으로 판단된다.
-
Comparison of Ground Response Characteristics of Liquefiable Soils in the Pohang Area Using 1D and 2D Numerical Analyses
-

-
Evaluation of Seismic Collapse Behavior of an Embankment Slope Using a 1 g Shaking Table
1g 진동대를 활용한 지진 발생 시 성토 사면의 붕괴 특성 평가
-
Sugeun Jeong, Hoyeon Kim, Daehyeon Kim
정수근, 김호연, 김대현
- Seismic design of slope ground is commonly performed using simplified approaches such as pseudo-static analysis. However, these methods have limitations in accurately …
사면 지반의 내진설계는 대부분의 실무자들이 유사 정적 해석과 같은 단순화한 방법으로 설계를 진행해왔다. 하지만 이러한 단순화된 방법은 실제 현장 조건을 완벽히 재현하는데 …
- Seismic design of slope ground is commonly performed using simplified approaches such as pseudo-static analysis. However, these methods have limitations in accurately reproducing actual field behavior during earthquakes. To address these limitations, seismic intensity measures have been proposed to quantify ground motion characteristics related to damage, including energy and duration. Despite their usefulness, such indices are difficult to evaluate accurately using field observations or simplified analysis methods and may not fully represent the energy involved in actual slope collapse. In this study, a full-scale 1:1 embankment slope model was constructed and tested using a 1 g shaking table. By applying controlled seismic excitation, the influence of various seismic intensity measures on slope behavior was examined by comparing their values at the onset of cracking and collapse. Based on measured accelerations, Arias intensity (ARI), Cumulative absolute (CAV), Vibration dose value (VDV), and Root mean square acceleration (Arms) were selected and analyzed. Under input ground motions of 10 Hz at 0.2 g and 0.28 g, only cracking occurred, whereas clear collapse was observed at 10 Hz and 0.3 g and at 20 Hz and 0.4 g. Minor surface cracks were found to have limited influence on slope behavior and seismic response measures. Among the evaluated indices, ARI and VDV showed clear sensitivity to both cracking and collapse, while CAV and Arms exhibited relatively minor changes. These results indicate that ARI and VDV most effectively reflect embankment slope damage.
- COLLAPSE
사면 지반의 내진설계는 대부분의 실무자들이 유사 정적 해석과 같은 단순화한 방법으로 설계를 진행해왔다. 하지만 이러한 단순화된 방법은 실제 현장 조건을 완벽히 재현하는데 많은 한계가 존재한다. 이러한 한계들을 지진 강도 지표(Seismic intensity measure)를 통해 지반운동의 세기를 수치화해 손상 가능성에 대하여 설명하고 예측하기 위한 지표들을 꾸준히 연구해 왔다. 이러한 지표는 지진 발생 시 지반운동의 에너지, 지속시간과 같은 성분들을 정량적으로 표시할 수 있다. 하지만 이러한 수치들도 실제 현장에서의 관측의 어려움과 유사 정적과 같은 해석의 해석 방법으로는 실제 붕괴 시 발생하는 지진 에너지에 대해 정밀하게 나타내는 데에는 많은 한계가 있다. 본 연구에서는 1g 진동대에서 조성한 1:1 모형 성토사면을 대상으로, 입력 지진동 조건 변화에 따른 사면의 균열 및 붕괴 시 지진 강도 지표의 관계를 분석하였다. 입력 지진동은 10Hz 0.2g, 0.28g, 0.3g 및 20Hz 0.4g의 정현파로 구성하였으며, 계측 가속도를 이용해 Arias intensity(ARI), Cumulative absolute(CAV), Vibration dose value(VDV), Root mean square acceleration(Arms)를 산정하여 시간 이력으로 비교하였다. 실험 결과, 10Hz 0.2와 0.28g에서는 사면 표면에 미세한 균열만 발생하여 가속도 및 지진 강도 지표의 변화가 제한적으로 나타났다. 반면 10Hz 0.3g와 20Hz 0.4g에서는 사면에 뚜렷한 붕괴가 발생하였고, 이 시점에서 가속도 진폭이 급격히 증가하였다. 특히 ARI와 VDV는 균열과 붕괴 발생 시점에 민감하게 반응하여 CAV와 Arms에 비해 사면의 손상 정도를 더 명확히 반영하는 것으로 확인되었다. 이러한 결과는 성토사면의 실험적 붕괴 특성 평가 및 지진 재해 위험성 검토 시 ARI와 VDV를 우선적인 지진 강도 지표로 활용할 수 있음을 시사하는 것으로 판단된다.
-
Evaluation of Seismic Collapse Behavior of an Embankment Slope Using a 1 g Shaking Table
-
-
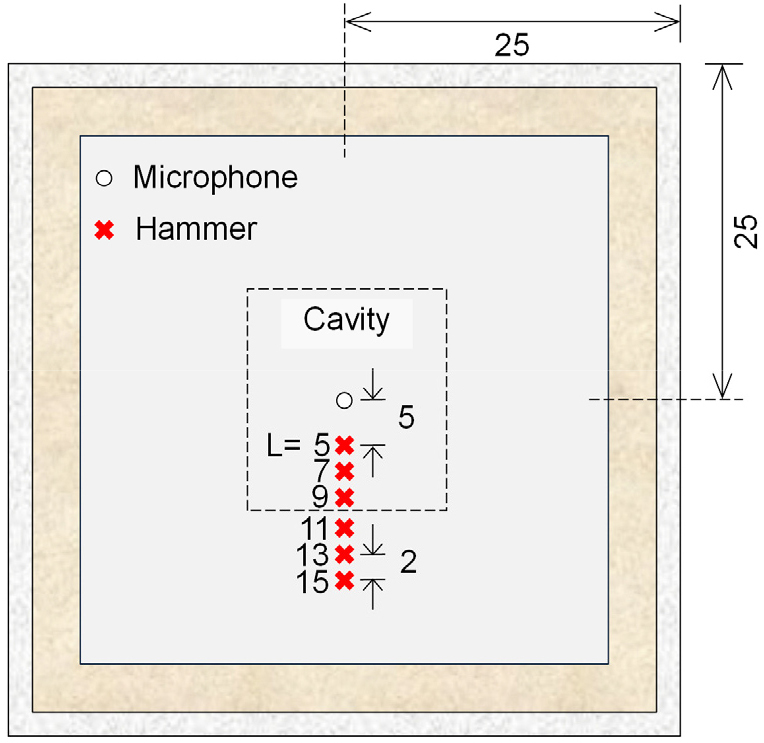
Effect of Impact System Parameters on Microphone-Based Detection of Subsurface Cavities behind Wall Structures
벽체 하부 공동 검측을 위한 음파 탐사시 타격 시스템의 영향
-
Jeong Eon Park, Jong-Sub Lee, Hoang Ngoc Quy, Seonghun Kang
박정언, 이종섭, 호앙녹퀴, 강성훈
- Depth of a cavity behind a wall structure is a primary factor in assessing risk, so evaluating detectability versus depth is essential. …
벽체 구조물 배면의 공동 깊이는 공동의 위험도와 직결되므로, 공동 깊이에 따른 공동 검측 가능성에 대한 연구가 필수적이다. 본 연구에서는 공동 중심과 타격 …
- Depth of a cavity behind a wall structure is a primary factor in assessing risk, so evaluating detectability versus depth is essential. This laboratory study examined how impact system parameters influence cavity detection using microphone measurements. Parameters include the distance between the cavity center and impact point, hammer tip material, and wall thickness. A model chamber with a simulated wall and adjustable cavity depth was used. Acoustic signal and impact loads were measured while varying top-plate thickness and hammer tip material. Flexibility was derived from the measured signals and compared across test conditions. Results show that measured flexibility increased as the impact point approached the cavity center, and that a rubber hammer tip produced deeper-penetration responses than a plastic tip. These findings indicate that microphone-based methods can effectively detect deep cavities behind wall structures.
- COLLAPSE
벽체 구조물 배면의 공동 깊이는 공동의 위험도와 직결되므로, 공동 깊이에 따른 공동 검측 가능성에 대한 연구가 필수적이다. 본 연구에서는 공동 중심과 타격 지점 간의 거리, 해머 팁 재질, 벽체 두께와 같은 타격 시스템 변수들이 공동 검측 가능성에 미치는 영향을 평가하고자 실내 실험을 수행하였다. 모형 공동과 벽체를 포함한 토조를 조성하였으며, 상부 판으로부터의 거리를 조절하며 토조 내에 모형 공동을 매설함으로써 서로 다른 깊이의 공동을 모사하였다. 상부 판의 두께 및 해머 팁 재질을 변화시켜 음파 신호를 측정하였다. 본 연구에서는 구조물에 단위 하중이 가해졌을 때 발생하는 처짐과 동일한 개념인 유연성 값을 측정된 음파 및 하중 신호를 활용하여 산정하였으며, 이를 바탕으로 타격 시스템 변수에 따른 유연성 변화를 비교 분석하였다. 실험 결과 타격 지점이 공동 중심에 근접할수록 유연성이 크게 나타났으며, 고무 팁이 플라스틱 팁에 비해 더 깊은 가탐 깊이를 보였다. 본 연구는 마이크로폰이 벽체 배면의 깊은 공동을 검측하기 위해 유용하게 이용될 수 있음을 보여준다.
-
Effect of Impact System Parameters on Microphone-Based Detection of Subsurface Cavities behind Wall Structures
-
-
Evaluation of AI-Based Prediction for Ground Subsidence and Its Feature Importance Analysis Using Imbalanced Multivariate Data
불균형 다변량 데이터를 활용한 인공지능 기반 지반함몰 예측 성능 분석 및 변수 중요도 해석
-
YuJin Kim, Hyobum Lee, Sung Jin Lee, SeonHong Na
김유진, 이효범, 이성진, 나선홍
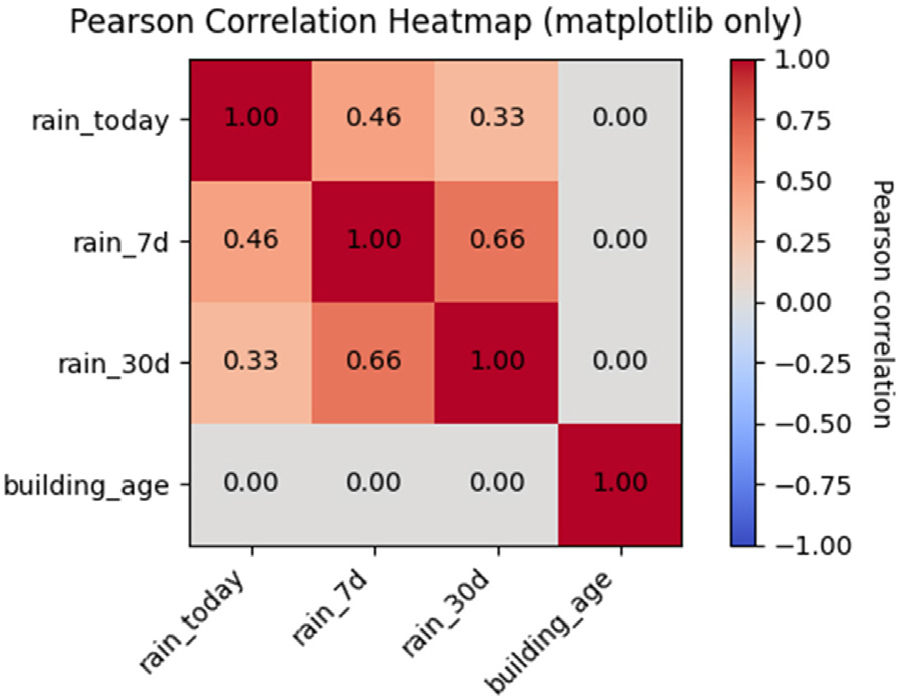
- This study evaluates the probability of ground subsidence and examines the applicability of AI-based prediction models using publicly available data. Gwangju Metropolitan …
본 연구에서는 공공데이터를 활용하여 지반함몰 발생 가능성 분석하고, 인공지능 기반 예측 모델의 적용성을 평가하였다. 연구 대상 지역으로 광주광역시를 선정하고, 최근 5년간(2019-2023) 보고된 …
- This study evaluates the probability of ground subsidence and examines the applicability of AI-based prediction models using publicly available data. Gwangju Metropolitan City was selected as the study area, and a spatial dataset was constructed using five years of ground subsidence records (2019–2023), rainfall data (including 7-day and 30-day cumulative rainfall), geological information, and the distribution of aged buildings. To address severe class imbalance, techniques including undersampling, the synthetic minority oversampling technique, class weighting, and focal loss were applied. A comparative analysis was then performed using Random Forest, XGBoost, and deep neural networks. Although overall F1-scores were constrained by the intrinsic rarity of subsidence events, precision–recall analysis demonstrated that the models achieved meaningful classification performance. Among the evaluated models, XGBoost exhibited the most stable and accurate predictive capability. Feature importance analysis identified cumulative rainfall and the number of aged buildings as the most influential variables, indicating that urban ground subsidence is predominantly governed by the combined effects of long-term rainfall accumulation and aging underground infrastructure.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구에서는 공공데이터를 활용하여 지반함몰 발생 가능성 분석하고, 인공지능 기반 예측 모델의 적용성을 평가하였다. 연구 대상 지역으로 광주광역시를 선정하고, 최근 5년간(2019-2023) 보고된 지반함몰 사례를 기반으로 강수량, 노후건물수, 지질정보 등의 변수를 수집하여 공간 데이터셋을 구축하였다. 지반함몰 발생 비율이 극히 낮은 불균형한 데이터 특성을 고려하여 언더샘플링(Undersampling), SMOTE, 클래스 가중치(Class weight), Focal loss 등의 다양한 불균형 처리 기법을 적용하였으며, DNN, Random Forest, XGBoost 모델을 이용해 예측 성능을 비교·분석하였다. 분석 결과, 전체적인 F1-score는 낮게 나타났으나, 정밀도-재현율(Precision-Recall) 곡선을 통해 분류 성능이 유의미한 수준임을 확인하였으며, 트리 기반의 XGBoost 모델이 가장 안정적이고 우수한 성능을 보였다. 변수 중요도 분석에서는 누적 강수량(7일, 30일)과 노후건물수가 주요 영향인자로 도출되었다. 이는 지반함몰이 단기적 요인보다는 장기적인 누적 강우와 노후화된 인공 구조물의 복합적 상호작용에 의해 발생함을 시사한다.
-
Evaluation of AI-Based Prediction for Ground Subsidence and Its Feature Importance Analysis Using Imbalanced Multivariate Data
-
-
Quantitative Assessment of Crack Density Considering Weathering-Induced Uncertainty in Rock Properties
입력 물성 변동이 균열밀도 예측에 미치는 영향: 물리 기반 탄력도와 기계학습 중요도 비교
-
Hyung-Koo Yoon
윤형구
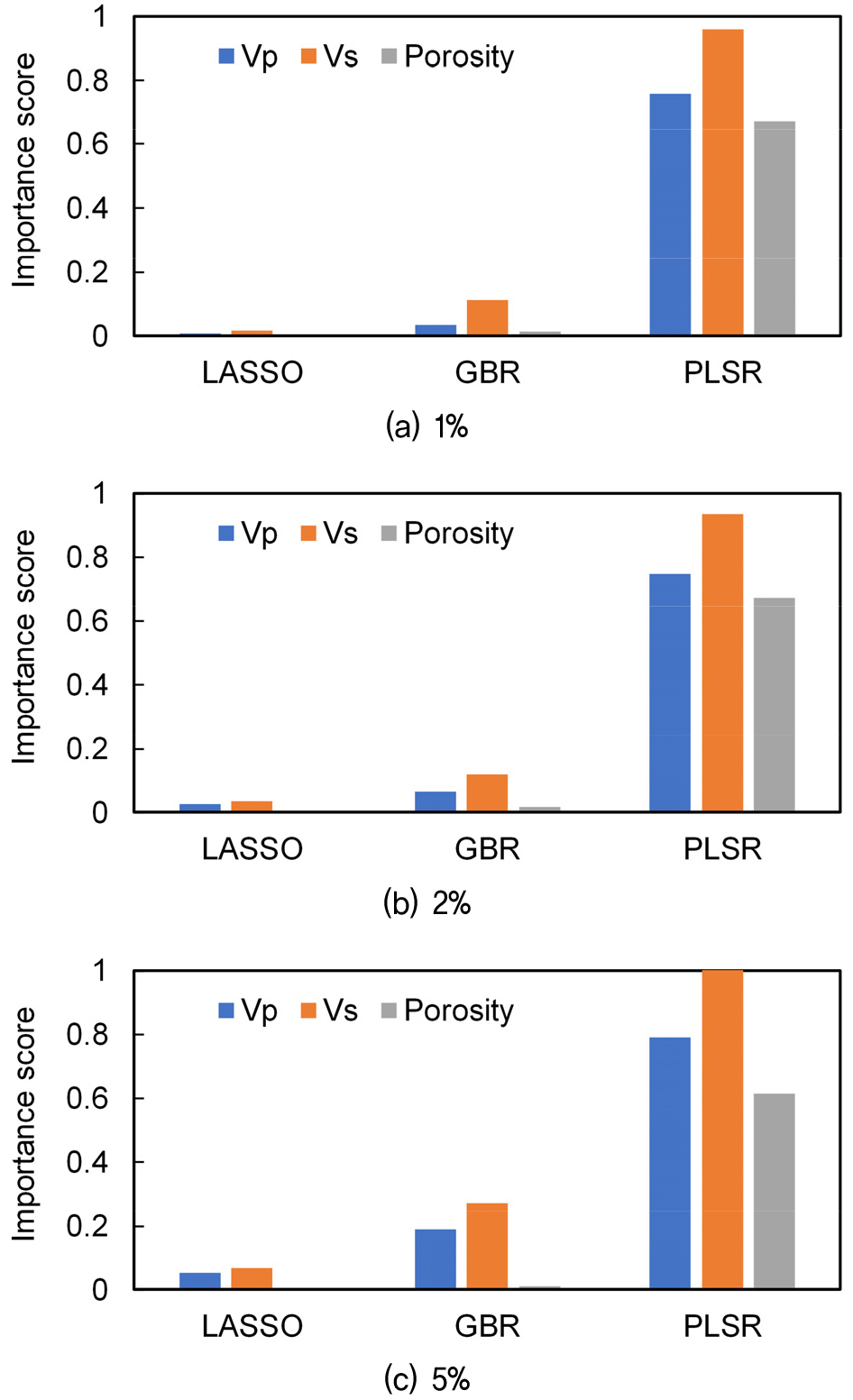
- Crack density is a key indicator for evaluating the dynamic and elastic behavior of rock and soil materials, and is closely linked …
균열밀도는 암반 및 지반 재료의 동적·탄성적 거동을 평가하는 핵심 지표로, 압축파 속도(Vp), 전단파 속도(Vs) 그리고 간극률(φ)과 밀접하게 연관된다. 본 연구에서는 풍화 실험 …
- Crack density is a key indicator for evaluating the dynamic and elastic behavior of rock and soil materials, and is closely linked to compressional wave velocity (Vp), shear wave velocity (Vs), and porosity (φ). In this study, laboratory weathering test data were expanded into Monte Carlo–augmented datasets by introducing 1%, 2%, and 5% uncertainty into the input properties. The structural sensitivity of the crack density equation and the data-driven sensitivity derived from machine learning methods were jointly analyzed to examine the influence of each input variable. The physics-based elasticity analysis shows that crack density is most sensitive to Vp on a global scale, while Vs exhibits marked local sensitivity under specific conditions; in contrast, the influence of φ remains minimal. The AI-based importance analysis similarly identifies Vp and Vs as the dominant predictors of crack density across all three algorithms, consistent with the physics-based results. Moreover, the relative importance of Vs increases as the uncertainty level (σ) grows, reflecting the nonlinear sensitivity amplification observed in elasticity evaluation. Overall, this study demonstrates that the structural characteristics of the physical model and the empirical sensitivities derived from data-driven methods are complementary, providing insights that strengthen reliability assessment of crack density prediction models and inform management of input material properties.
- COLLAPSE
균열밀도는 암반 및 지반 재료의 동적·탄성적 거동을 평가하는 핵심 지표로, 압축파 속도(Vp), 전단파 속도(Vs) 그리고 간극률(φ)과 밀접하게 연관된다. 본 연구에서는 풍화 실험 데이터를 기반으로 입력 물성에 1%, 2%, 5% 수준의 불확실성을 부여하여 Monte Carlo 기반 증폭 데이터를 구축하고, 균열밀도 산정식의 구조적 민감도와 데이터 기반 민감도를 종합적으로 분석하여 입력 인자의 영향성을 고찰하는 것이다. 우선, 물리식 기반 탄력도를 통해 ε이 입력 변수에 대해 갖는 국소 민감도를 정량화한 결과, 균열밀도는 전역적으로 Vp에 가장 강하게 반응하며, Vs는 특정 조건에서 매우 높은 국소 민감도를 보이는 반면 φ는 기여도가 제한적이었다. 이어서 AI 기반 변수 중요도 분석을 수행한 결과, 세 알고리즘 모두 Vp와 Vs를 균열밀도 예측의 주요 변수로 식별하여 물리 기반 분석과 일관된 결론을 제시하였다. AI 분석에서는 σ 증가에 따라 Vs의 중요도가 상대적으로 크게 증가하는 경향이 관찰되었으며, 이는 탄력도 분석에서 확인된 Vs의 비선형 민감도 확장과 정확히 대응하였다. 본 연구는 물리 모델의 구조적 특성과 데이터 기반 경험적 민감도가 상호 보완적으로 해석될 수 있음을 보여주었으며, 균열밀도 예측 모델의 신뢰성 평가 및 입력 물성 관리에 기여할 수 있다.
-
Quantitative Assessment of Crack Density Considering Weathering-Induced Uncertainty in Rock Properties
-
-
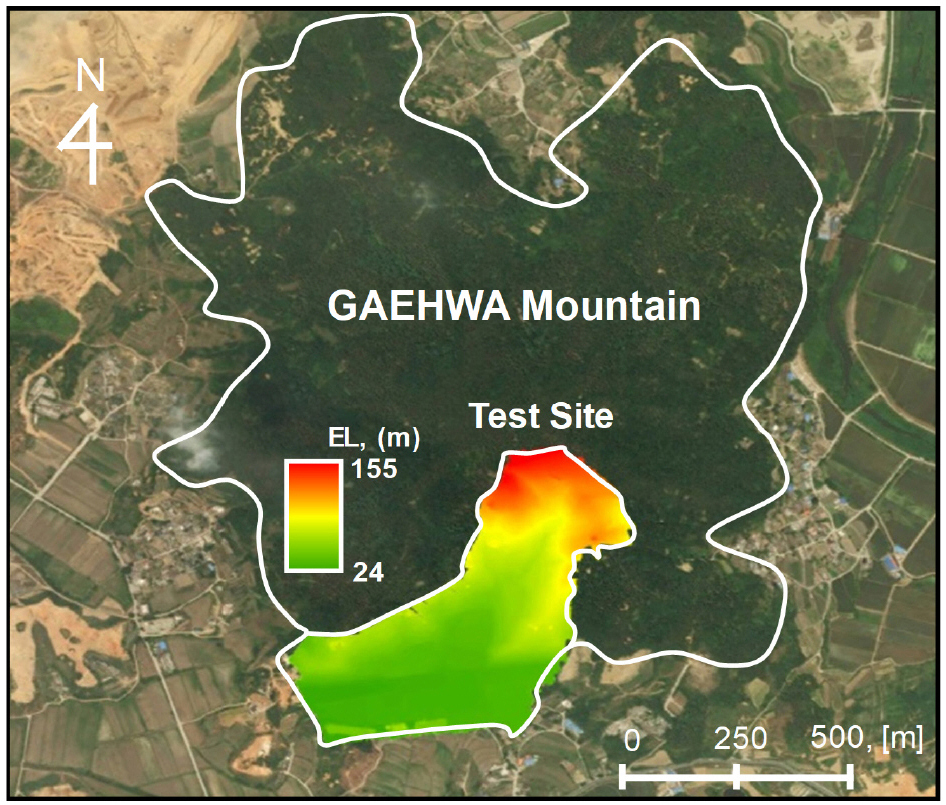
DEM Generation from CubeSat Imagery via Photogrammetry
CubeSat 위성 영상 활용한 Digital Elevation Model(DEM) 생성
-
Sang-Hyun Park, Jun-Woo Shin, Kyungwon Park, Boo Hyun Nam
박상현, 신준우, 박경원, 남부현
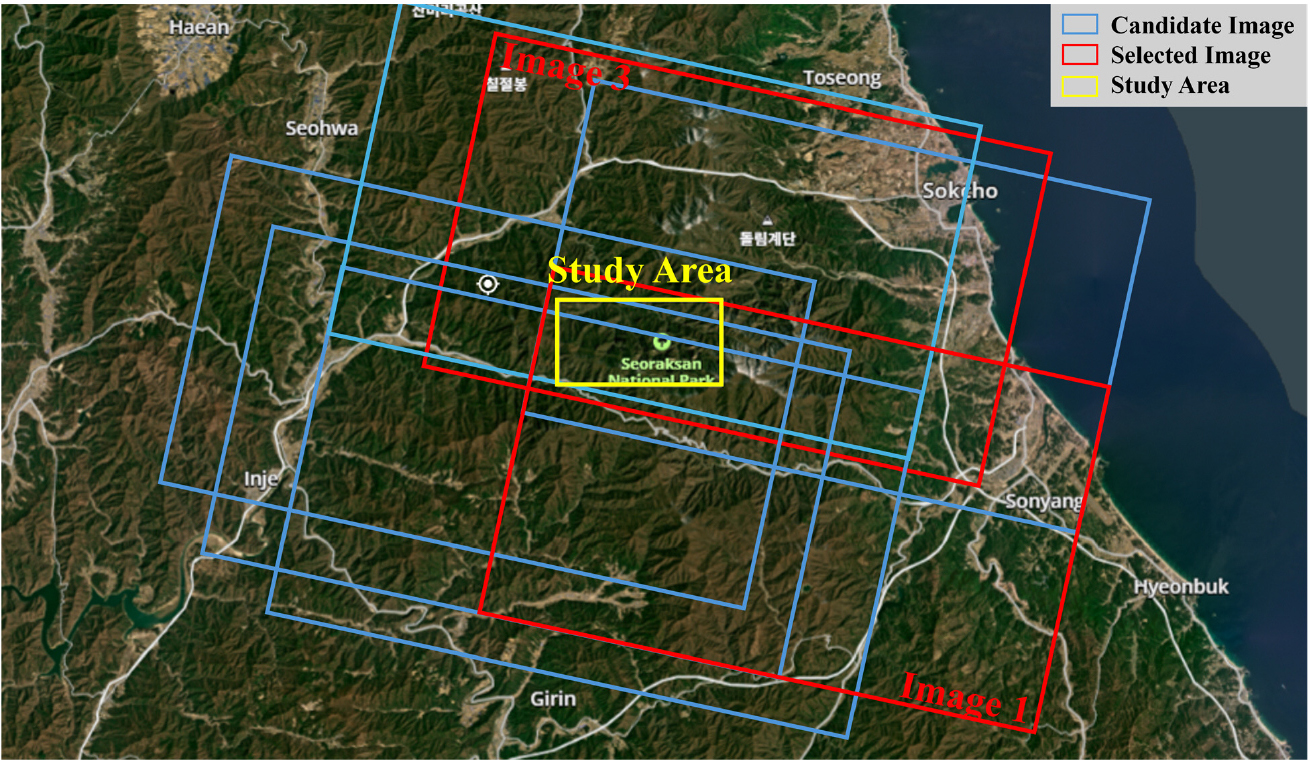
- High-resolution digital elevation models (DEMs) are essential for hazard assessment and monitoring, but conventional methods such as aerial LiDAR or commercial satellites …
고해상도 수치표고모델(Digital Elevation Model, DEM)은 재난 대응 및 지형 변화 탐지에 필수적이나, 기존 항공 LiDAR나 상용 위성은 높은 비용과 시간 제약으로 신속한 …
- High-resolution digital elevation models (DEMs) are essential for hazard assessment and monitoring, but conventional methods such as aerial LiDAR or commercial satellites can be costly and slow. This study generates and evaluates a high-resolution DEM from a single PlanetScope stereo pair to offer a rapid, low-cost alternative. Using photogrammetric processing, a 4-m DEM was produced for Seoraksan National Park and compared with lower-resolution DEMs (SRTM 30 m, NGII 90 m). The CubeSat-derived DEM captured detailed valleys and ridges omitted in low-resolution models. Results demonstrate that a single CubeSat stereo pair can produce 3D terrain information suitable for rapid, economical updating and monitoring of complex mountainous terrain, for use in landslide and flood response.
- COLLAPSE
고해상도 수치표고모델(Digital Elevation Model, DEM)은 재난 대응 및 지형 변화 탐지에 필수적이나, 기존 항공 LiDAR나 상용 위성은 높은 비용과 시간 제약으로 신속한 데이터 확보에 한계가 있다. 본 연구는 이러한 한계를 극복하고자, 저비용·고빈도로 전 지구를 촬영하는 초소형 위성(CubeSat) PlanetScope의 단일 스테레오 영상을 활용하여 고해상도 DEM을 생성 및 평가하는 것을 목적으로 한다. 이를 위해 설악산 국립공원을 대상으로, 적합한 스테레오 영상 쌍에 사진측량(Photogrammetry) 기법을 적용하여 4m DEM을 생성하였다. 생성된 DEM을 기존 저해상도 DEM(SRTM 30m, NGII 90m) 및 원본 영상과 비교한 결과, 본 연구에서 생성된 DEM이 저해상도 DEM에서 생략된 계곡과 능선을 명확히 묘사함을 확인하였다. 본 연구 결과는 CubeSat 단일 스테레오 영상만으로도 복잡한 산악 지형의 3D 정보 생성이 가능함을 입증하였으며, 향후 CubeSat을 통한 신속하고 경제적인 지형 데이터 갱신 및 산사태·홍수 등 재난 지역 모니터링에 효과적으로 활용될 수 있을 것이다.
-
DEM Generation from CubeSat Imagery via Photogrammetry
-
-
Analysis of Pile Foundation Behavior under Different Superstructure Load Conditions in Vertical Extension Remodeling
수직증축 리모델링 시 상부하중 형태에 따른 말뚝기초 거동 분석
-
Yu-Jin Noh, Se-Na Eom, Jong-Jeon Park, Jung-Hwan Kim, Jae-Hwan Lee, Jun-Young Ko
노유진, 엄세나, 박종전, 김정환, 이재환, 고준영
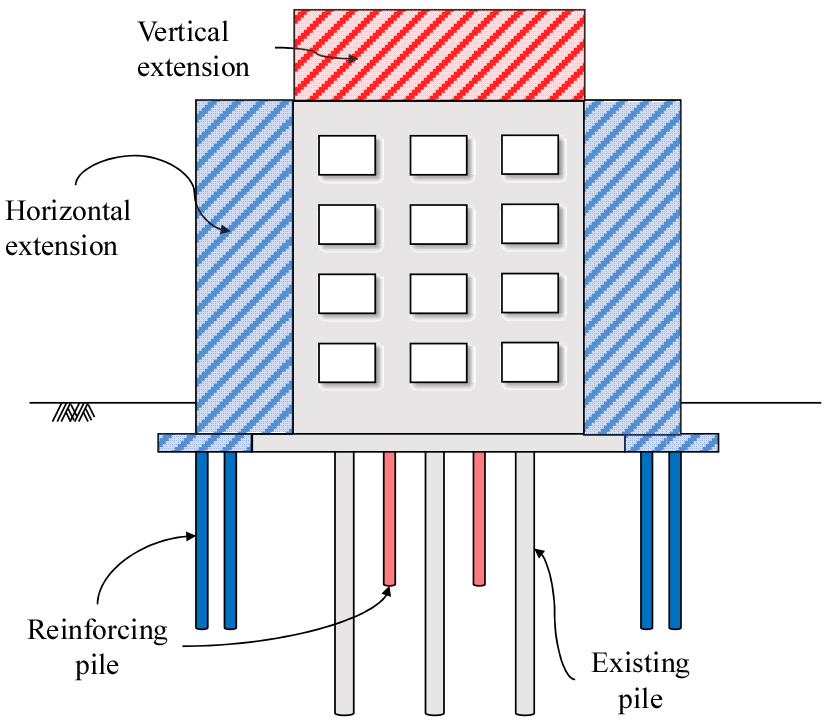
- This study investigates the influence of superstructure load modeling and raft stiffness (rigid and flexible) on the behavior of piled raft foundations …
본 연구에서는 수직증축 리모델링 시 상부하중 모델링 형태와 기초판의 강성 및 연성이 말뚝지지 전면기초 거동에 미치는 영향을 분석하고자 PLAXIS 3D를 이용한 유한요소해석을 …
- This study investigates the influence of superstructure load modeling and raft stiffness (rigid and flexible) on the behavior of piled raft foundations during vertical extension remodeling using three-dimensional finite element analysis with PLAXIS 3D. The ground profile consisted of weathered soil and weathered rock layers. The foundation system included a square raft measuring 18 m × 18 m × 1 m, 81 existing piles (PC piles), and 64 reinforcing piles (micropiles). Superstructure loads were modeled as Full Distributed Load (FDL), Column Load, Wall Load, and Partial Distributed Load (PDL; C100/C70/C50). Numerical analyses were performed according to the construction stages of vertical extension. The results indicate that, for a rigid raft, settlement was relatively uniform regardless of the load modeling method, and differences in pile axial forces compared with the FDL case were within 2% for existing piles and 18% for reinforcing piles. In contrast, a flexible raft exhibited pronounced differential settlement and increased axial forces in central piles under PDL conditions due to load concentration in the core area. These findings suggest that both superstructure load modeling and raft stiffness should be carefully considered when designing foundation reinforcement for vertical extension remodeling.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구에서는 수직증축 리모델링 시 상부하중 모델링 형태와 기초판의 강성 및 연성이 말뚝지지 전면기초 거동에 미치는 영향을 분석하고자 PLAXIS 3D를 이용한 유한요소해석을 수행하였다. 지반은 풍화토과 풍화암으로 구성하였고, 기초는 18m × 18m × 1m 기초판과 기존말뚝(PC 말뚝) 81본, 보강말뚝 64본(마이크로파일)로 구성하였다. 상부하중은 전체 등분포하중(FDL), 기둥하중(CL), 벽체하중(WL), 부분 등분포하중(PDL;C100/C70/C50)으로 고려하고, 수직증축 시공단계에 따라 해석을 수행하였다. 해석 결과, 강성 기초판에서는 하중 모델링 방식에 관계없이 침하량은 균등하고, 축력의 경우 전체 등분포 하중 대비 기존말뚝 2%, 보강말뚝은 18% 이내로 축력 차이가 발생하였다. 연성 기초판에서는 부분 등분포하중 조건에서 코어부 집중하중의 영향으로 부등침하 및 중앙부 말뚝의 축력이 크게 나타났다. 따라서, 수직증축 리모델링을 위한 보강 기초 설계 시 상부하중 모델링 형태와 기초판 특성을 함께 고려해야할 것으로 사료된다.
-
Analysis of Pile Foundation Behavior under Different Superstructure Load Conditions in Vertical Extension Remodeling
-
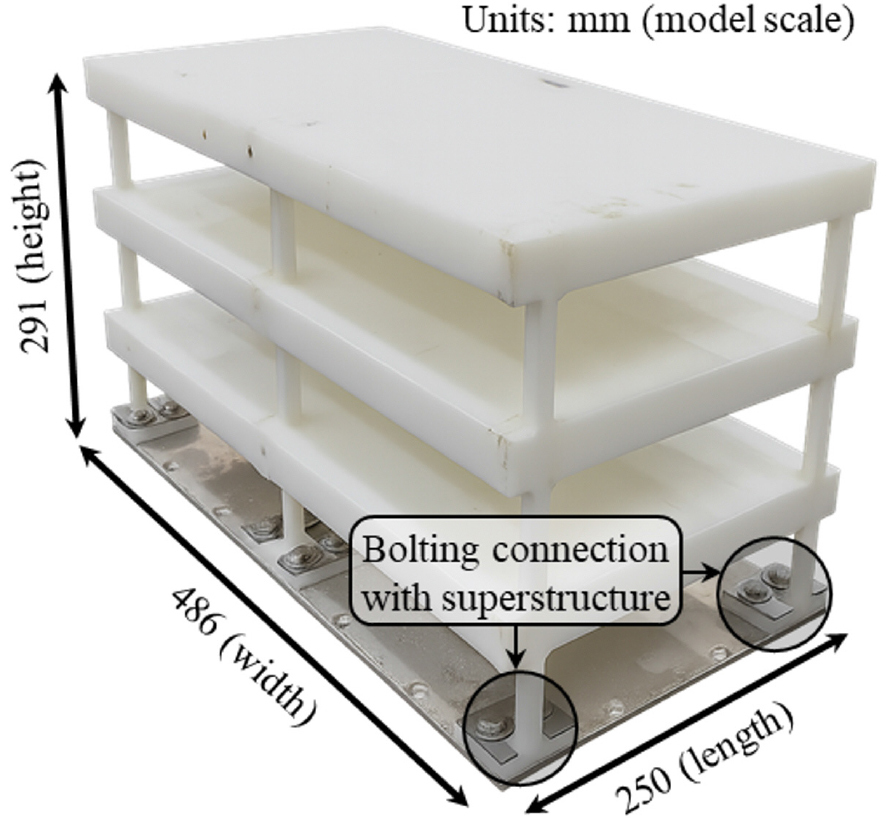
-
Effects of Nonliquefiable Crust on Liquefaction-Induced Settlement of Shallow Foundations
표층 비액상화층이 얕은기초 건축물의 액상화 침하 거동에 미치는 영향
-
Tae-Hun Hwang, Nguyen Quang-Thien-Buu, Dae-Yeong Kim, Sung-Ryul Kim
황태훈, 응위엔부치앙, 김대영, 김성렬
- Field observations have shown that a nonliquefiable crust can mitigate liquefaction damage by confining liquefaction to the underlying liquefiable layer. However, the …
지표면에 위치한 비액상화층은 지진 시 액상화를 하부의 느슨한 모래층으로 국한하여 피해를 저감한다는 현장 관측이 반복적으로 보고되었다. 또한, 이러한 다층지반 조건에서 얕은기초 건축물의 …
- Field observations have shown that a nonliquefiable crust can mitigate liquefaction damage by confining liquefaction to the underlying liquefiable layer. However, the complexity of soil–structure interaction for shallow foundations under multilayered ground conditions remains insufficiently understood. This study evaluated the influence of a nonliquefiable crust on liquefaction-induced settlement of shallow foundations using 1-g shaking table model tests. A three-story, multi-degree-of-freedom superstructure supported by a shallow foundation was employed to capture soil–structure interaction effects. Two ground conditions, without and with a 90-mm-thick nonliquefiable crust, were tested under sinusoidal input motion. Excess pore pressure and settlement time histories were measured in the free field and beneath the foundation and were interpreted in three phases: (1) during shaking, (2) dissipation within the liquefiable layer, and (3) dissipation within the nonliquefiable crust. Experimental results indicated that the nonliquefiable crust reduced total settlement by 63% in the free field and by 40% beneath the shallow foundation. In addition, it shifted the dominant free-field settlement from Phase 1 (during shaking) to Phases 2 and 3 (post-shaking), as additional post-shaking settlement developed within the nonliquefiable crust. In contrast, foundation settlement was governed by shear-induced settlement associated with the superstructure, resulting in most of the settlement occurring during shaking, regardless of the presence of the nonliquefiable crust.
- COLLAPSE
지표면에 위치한 비액상화층은 지진 시 액상화를 하부의 느슨한 모래층으로 국한하여 피해를 저감한다는 현장 관측이 반복적으로 보고되었다. 또한, 이러한 다층지반 조건에서 얕은기초 건축물의 지반-구조물 상호작용은 더욱 복잡하게 나타난다. 본 연구는 1-g 진동대 모형실험을 통해 표층 비액상화층이 얕은기초 건축물의 액상화 유발 침하에 미치는 영향을 평가하였다. 얕은기초 3층 구조물을 대상으로, 표층 비액상화층이 없는 경우와 90 mm 두께의 비액상화층이 존재하는 두 조건에 대해 동일한 정현파를 적용하였다. 자유장 및 얕은기초 하부에서 과잉간극수압과 침하를 계측하고, 침하를 (1) 진동 중, (2) 액상화층 소산, (3) 표층 비액상화층 소산의 세 단계로 구분하여 해석하였다. 실험 결과, 표층 비액상화층은 자유장 침하를 63%, 얕은기초 침하를 40% 감소시켰다. 또한, 표층 비액상화층이 존재하는 조건에서는 진동 후 표층 비액상화층의 소산에 의한 추가 침하가 발생함에 따라, 자유장의 주된 침하 시점이 1단계(진동 중)에서 2, 3단계(진동 후)로 전이되었다. 반면, 얕은기초 침하는 지반–구조물 상호작용에 의한 전단 유발 침하가 주된 메커니즘으로 작용하여, 표층 비액상화층의 존재 여부와 무관하게 대부분의 침하는 1단계(진동 중)에서 발생하였다.
-
Effects of Nonliquefiable Crust on Liquefaction-Induced Settlement of Shallow Foundations
-

-
Field Study on the Correlation between Intelligent Compaction Measurement Values and Location-Specific In-Situ Test Results
현장시험을 통한 지능형 다짐값과 일점품질시험 간 상관성 평가
-
Sung-Ha Baek, Jin-Woo Cho
백성하, 조진우
- This study evaluates correlations between compaction meter value (CMV) and location-specific in-situ test results through field compaction tests. CMV, light-weight deflectometer, and …
본 연구에서는 현장시험을 통해 대표적인 지능형 다짐값(CMV)과 일점품질시험(들밀도시험, 평판재하시험, LWD 시험, DCP 시험) 간의 상관성을 체계적으로 평가했다. CMV 및 다수 지점에서 수행된 …
- This study evaluates correlations between compaction meter value (CMV) and location-specific in-situ test results through field compaction tests. CMV, light-weight deflectometer, and dynamic cone penetrometer results collected at multiple locations reflected improved average compaction quality with increasing roller passes, while their coefficients of variation (approximately 20–40%) revealed substantial spatial variability due to heterogeneity in fill material and moisture. In contrast, dry density and stiffness modulus values measured only twice per compaction stage did not show an increasing trend, indicating that a small number of in-situ tests cannot reliably represent compaction quality across a large construction area. Among point-by-point, all-average, and area-based correlation methods, the area-based method produced the highest correlations. Optimal region-of-interest (ROI) radii were determined as 1.5 m (dry density), 3.5 m (stiffness modulus), 2.5 m (ELWD), and 2.0 m (DPI). Based on these results, we propose a procedure to determine target CMV values by deriving a linear regression between average CMV within the optimal ROI and stiffness-based in-situ test results, thereby identifying target CMV values that satisfy the required quality criteria.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구에서는 현장시험을 통해 대표적인 지능형 다짐값(CMV)과 일점품질시험(들밀도시험, 평판재하시험, LWD 시험, DCP 시험) 간의 상관성을 체계적으로 평가했다. CMV 및 다수 지점에서 수행된 LWD와 DCP 시험 결과는 반복 다짐에 따른 평균적 다짐품질 향상을 명확히 반영했으며, 변동계수가 약 20~40% 범위로 나타나 성토재료 및 함수비 불균질성에 기인한 공간적 변동성이 매우 컸다. 반면, 각 단계에서 두 지점만 측정된 건조단위중량과 지지력계수는 다짐횟수 증가에 따른 뚜렷한 증가 경향을 보이지 않아, 제한된 일점품질시험만으로는 넓은 시공면의 다짐 상태를 대표하기 어렵다는 점이 드러났다. 단일점 기반 분석, 전체 평균 분석, 영역 기반 분석을 비교한 결과, 영역 기반 분석이 가장 높은 상관성을 보였으며, 최적 ROI 반경은 건조단위중량 1.5 m, 지지력계수 3.5 m, ELWD 2.5 m, DPI 2.0 m로 도출되었다. 이를 바탕으로 본 연구에서는 최적 ROI 내 CMV 평균값과 강성 기반 일점품질시험 결과 간의 선형 회귀식을 도출하고, 품질 기준을 만족하는 일점품질시험 값과 대응하는 CMV를 목표 지능형 다짐값으로 설정하는 절차를 제안했다.
-
Field Study on the Correlation between Intelligent Compaction Measurement Values and Location-Specific In-Situ Test Results
-
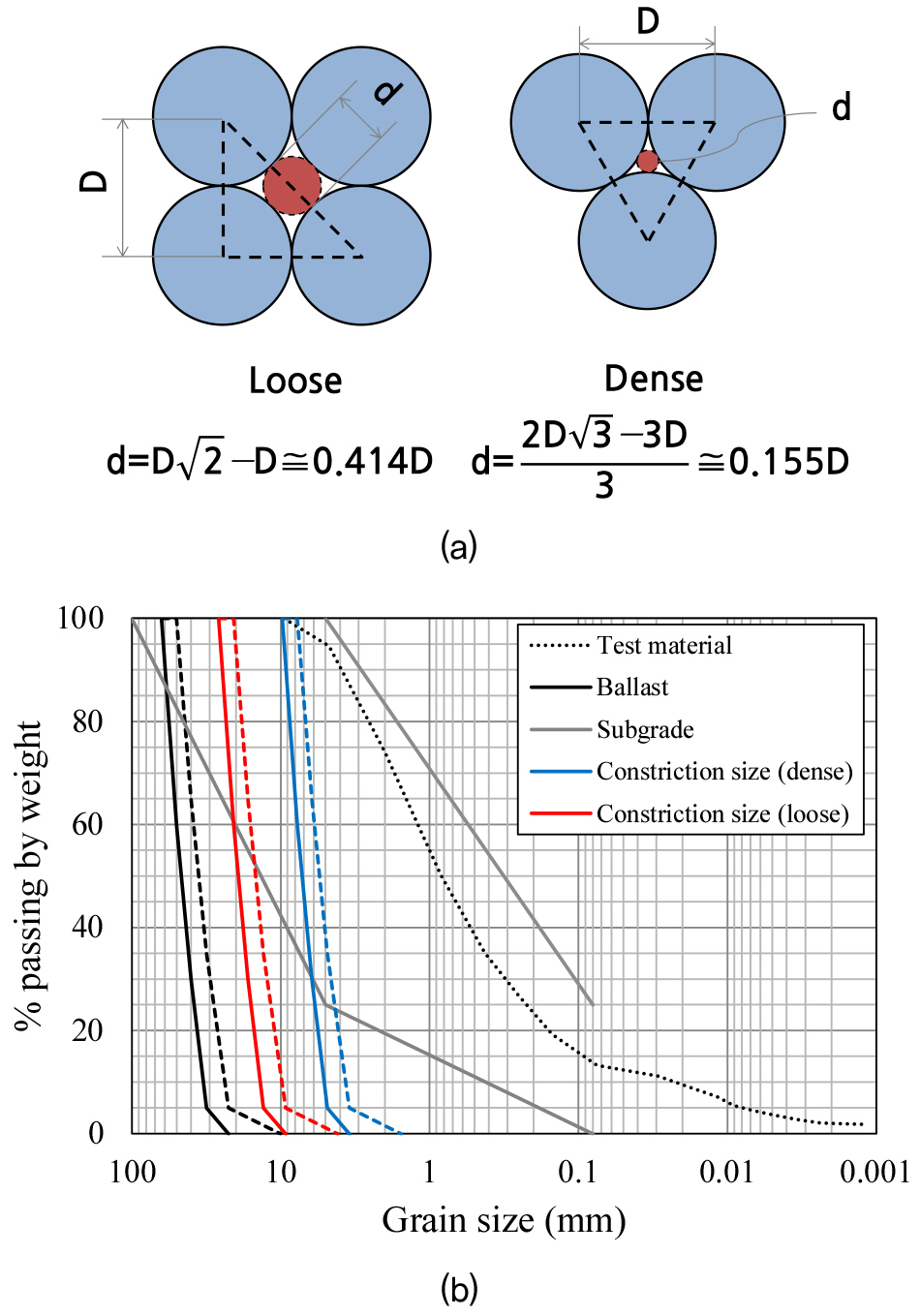
-
Analysis of Liquefaction Behavior of Subgrade Soils to Assess Mud Pumping Potential in Korean Ballasted Track Systems
자갈 궤도 분니 발생 가능성 평가를 위한 국내 철도설계기준 노반 흙의 액상화 거동 분석
-
Inhyun Kim, Hee-Jun Lee
김인현, 이희준
- Mud pumping denotes migration of fines from the subgrade into the ballast under repeated train loading, causing ballast fouling and track settlement. …
분니(mud pumping)는 열차 하중에 의해 노반 내에서 발생한 과잉간극수압으로 세립분이 도상에 유입되는 현상으로, 도상 오염과 자갈 도상의 침하를 유발한다. 일반적으로 분니는 투수계수가 …
- Mud pumping denotes migration of fines from the subgrade into the ballast under repeated train loading, causing ballast fouling and track settlement. Although mud pumping has traditionally been associated with low-permeability subgrades such as clays and poor drainage, recent work indicates that internally unstable soils with low fines content may also experience fluidization in the upper soil layers. To investigate this, cyclic triaxial tests were performed on subgrade samples conforming to the Korean Railway Design Standards to examine liquefaction and fluidization behavior. Internal instability and the potential migration of fines into the ballast were assessed. Results indicate that internally unstable soils exhibited fluidization in the upper specimen layers during cyclic loading, accompanied by significant increases in excess pore water pressure, and that fines were capable of migrating into the ballast layer. These findings show that mud pumping can occur because of internal instability even when fine content is relatively low.
- COLLAPSE
분니(mud pumping)는 열차 하중에 의해 노반 내에서 발생한 과잉간극수압으로 세립분이 도상에 유입되는 현상으로, 도상 오염과 자갈 도상의 침하를 유발한다. 일반적으로 분니는 투수계수가 낮고 배수가 불량한 점토질 노반에서 과잉간극수압 증가로 인해 발생하는 것으로 알려져 있으나, 최근 연구에서는 세립분 함량이 낮더라도 내부적으로 불안정한 흙에서는 상부의 액상화 및 유동화로 인해 분니가 발생할 수 있음이 보고되고 있다. 따라서 본 연구에서는 국내 철도설계기준을 만족하는 노반 재료를 대상으로 진동 삼축 실험을 수행하여 액상화 및 유동화 발생 여부를 평가하고, 노반의 내부불안정성과 도상자갈 사이 노반의 세립분 이동 가능성을 분석하였다. 그 결과 내부적으로 불안정한 시료의 경우, 진동 삼축 실험 시 시료 상단부의 유동화와 내부 과잉간극수압 증가를 확인하였고, 도상자갈 사이 노반의 세립분 이동이 가능하기 때문에 내부불안정성에 의한 분니 발생 가능성을 확인하였다.
-
Analysis of Liquefaction Behavior of Subgrade Soils to Assess Mud Pumping Potential in Korean Ballasted Track Systems
-
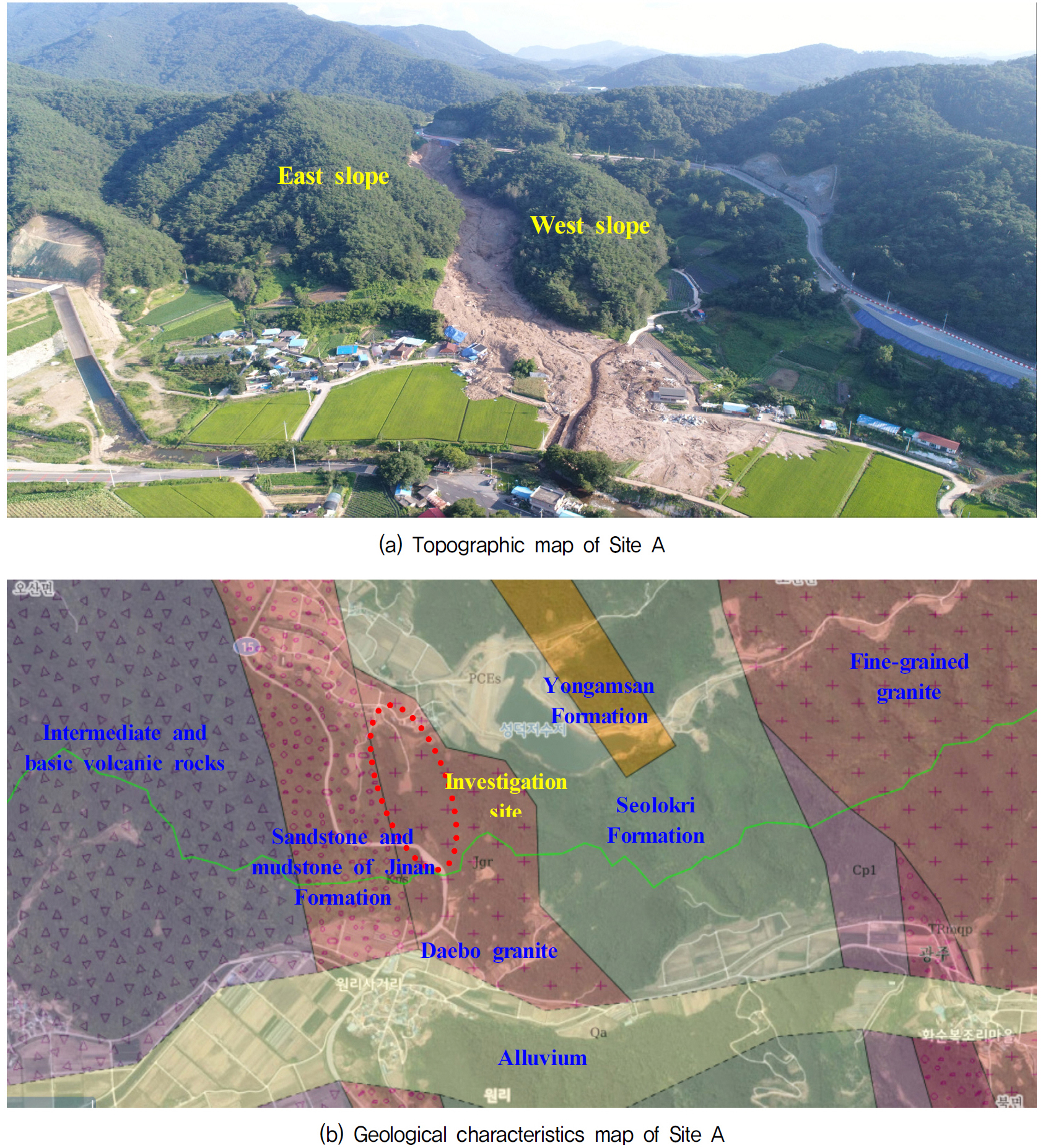
-
Statistical Analysis of Soil Characteristics Associated with Landslides in the Honam Region
통계기법을 이용한 호남지역 산사태의 토질특성 분석
-
Daehyeon Kim, Chanwook Jeong, Kyungho Park
김대현, 정찬욱, 박경호
- The study aims to identify soil characteristics associated with large-scale landslides that occurred in the Honam region. Major landslide cases on natural …
이 연구의 목적은 호남지역에서 발생한 대규모 산사태를 기반으로 산사태의 토질에 대한 특성을 분석하였다. 자연 사면에서 발생한 주요 산사태들은 산사태와 관련된 각 지질 …
- The study aims to identify soil characteristics associated with large-scale landslides that occurred in the Honam region. Major landslide cases on natural slopes were analyzed from a geotechnical perspective, with emphasis on soil properties related to geological conditions. In addition, statistical models were developed to estimate shear strength parameters, which are critical factors influencing landslide occurrence, based on correlations among key ground properties. Soil characteristics of gneiss and granite were analyzed in landslide-prone areas affected by heavy rainfall. The results show that gneiss soils exhibit higher void ratios and porosity, whereas granite soils have higher dry unit weights. Correlations among soil properties, permeability coefficient, and shear strength parameter were examined for landslide- affected slopes. Using the derived correlation equations, variations in shear strength were predicted based on changes in fundamental physical properties. Statistical analysis revealed that cohesion showed significant correlation with fine-grained soil content and uniformity coefficient, while internal friction angle was strongly correlated with void ratio, uniformity coefficient, and dry unit weight. Based on these relationships, simplified models were proposed to estimate shear strength parameters for granite and gneiss soil layers using basic physical property data. Further refinement of these models using additional landslide and geotechnical data from the Honam region is expected to improve their reliability and applicability.
- COLLAPSE
이 연구의 목적은 호남지역에서 발생한 대규모 산사태를 기반으로 산사태의 토질에 대한 특성을 분석하였다. 자연 사면에서 발생한 주요 산사태들은 산사태와 관련된 각 지질 유형의 토질 특성에 대한 정확한 분석을 통해 지반공학적 관점으로 분석하였다. 또한, 산사태의 주요 요인인 지반 매개변수의 특성 분석 결과를 바탕으로 산사태에 중요한 영향을 미치는 것으로 간주되는 전단강도를 쉽게 계산할 수 있는 모델을 제안하였다. 집중호우로 인해 산사태가 집중된 지역에서 지질 조건이 다른 편마암과 화강암의 토질 특성을 분석한 결과, 지질에 따라 다른 토질 특성을 보였다. 간극비와 공극률은 화강암 토질보다 편마암 토질에서 더 크고, 건조단위중량은 편마암 토질층보다 화강암 토질층에서 더 큰 것으로 나타났다. 산사태가 발생한 자연 사면의 토질층에서 토질 특성, 투수계수, 전단강도 매개변수 간의 상관관계를 분석하였고, 이로부터 도출된 상관 방정식을 사용하여 독립변수(기본 물리적 특성)의 변화로부터 종속변수(전단강도)의 변화를 예측하였다. 통계 기법을 사용하여 지반 매개변수와의 상관관계를 분석한 결과, 전단강도인 점착력은 세립토 함량 및 균등계수와 유의미한 상관관계가 있으며, 내부마찰각은 간극비, 균등계수, 건조단위중량과 유의미한 상관관계가 있는 것으로 나타났다. 화강암 및 편마암 토질층에 대해, 산사태 지역에서 중요하게 여겨지는 전단강도를 지반 매개변수와 유의미한 상관관계가 있는 물리적 특성 데이터만으로 쉽고 편리하게 추정할 수 있는 모델을 개발하였다(점착력 계산 모델 및 전단강도 계산 모델). 향후 호남지역에서 발생하는 산사태 데이터 및 지반정수를 추가함으로써 모델의 수정 및 보완을 통해 현재 모델의 신뢰성과 정확도를 향상시킬 것으로 기대된다.
-
Statistical Analysis of Soil Characteristics Associated with Landslides in the Honam Region
-
-
Analysis of Consolidation Characteristics of Soft Ground Using Field Instrumentation
현장계측을 이용한 연약지반의 압밀특성 분석
-
Daehyeon Kim, Hyeonseok Choi, Kyungho Park
김대현, 최현석, 박경호
- The southwestern coastal region of Korea consists largely of soft ground, and extensive residential and industrial development has been carried out there. …
국내 서남해안지역은 연약지반으로 구성되어 있으며 이 지역에 대한 택지 및 산업단지 조성이 활발히 실시되었었다. 연약지반 현장에서 단지 매립은 필수적으로 압밀침하에 대한 문제가 …
- The southwestern coastal region of Korea consists largely of soft ground, and extensive residential and industrial development has been carried out there. Land reclamation at soft-ground sites inevitably encounters consolidation settlement, which was investigated here using field instrumentation and analysis. However, conventional performance analyses based solely on settlement measurements often fall short because they do not account for excess pore water pressure dissipation. In this study, section P-1-1 at the site was instrumented, and the e-log p' method was applied to field data to predict final settlement prior to placing the final embankment. Results were compared with predictions from the theoretical hyperbolic method. The two methods produced similar results when pore water pressure had largely dissipated, or when the remaining residual pore pressure was negligible. Unlike the hyperbolic method, which evaluates final settlement only after embankment completion, the e-log p' method using field instrumentation allows construction of the virgin consolidation line and thus enables estimation of final settlement before completing the embankment.
- COLLAPSE
국내 서남해안지역은 연약지반으로 구성되어 있으며 이 지역에 대한 택지 및 산업단지 조성이 활발히 실시되었었다. 연약지반 현장에서 단지 매립은 필수적으로 압밀침하에 대한 문제가 발생하는데, 이에 따른 해결 방법으로 계측 및 분석을 수행하였다. 그러나 정확한 성과 분석은 기대에 미치지 못하였다. 이는 기존 연약지반의 압밀 특성 분석이 침하 형태에 따른 해석으로 국한되어 있어 과잉간극수압의 소산에 따른 과정이 해석 과정에 반영되어 있지 못하였기 때문이다. 따라서 본 연구에서는 현장 P-1-1구간을 지정하여 현장 계측자료를 이용한 e-log p' 법을 이용하여 압밀시험과 이론식인 쌍곡선법과 비교하여 최종성토 이전에 최종 침하량 예측하고자 하였다. e-log p' 법과 쌍곡선법 비교 분석결과, 간극수압이 소산되거나 잔류 간극수압이 거의 남지 않을 때 쌍곡선법의 결과와 e-log p' 법의 결과는 유사하였다. 또한, 쌍곡선법은 최종성토 이후에나 최종 침하량 평가가 가능하나, 현장 계측자료를 이용한 e-log p' 법은 최종성토 이전 처녀압밀선의 작도가 가능하므로 최종성토 이전에 최종 침하량 평가가 가능한 것으로 기대된다.
-
Analysis of Consolidation Characteristics of Soft Ground Using Field Instrumentation
-
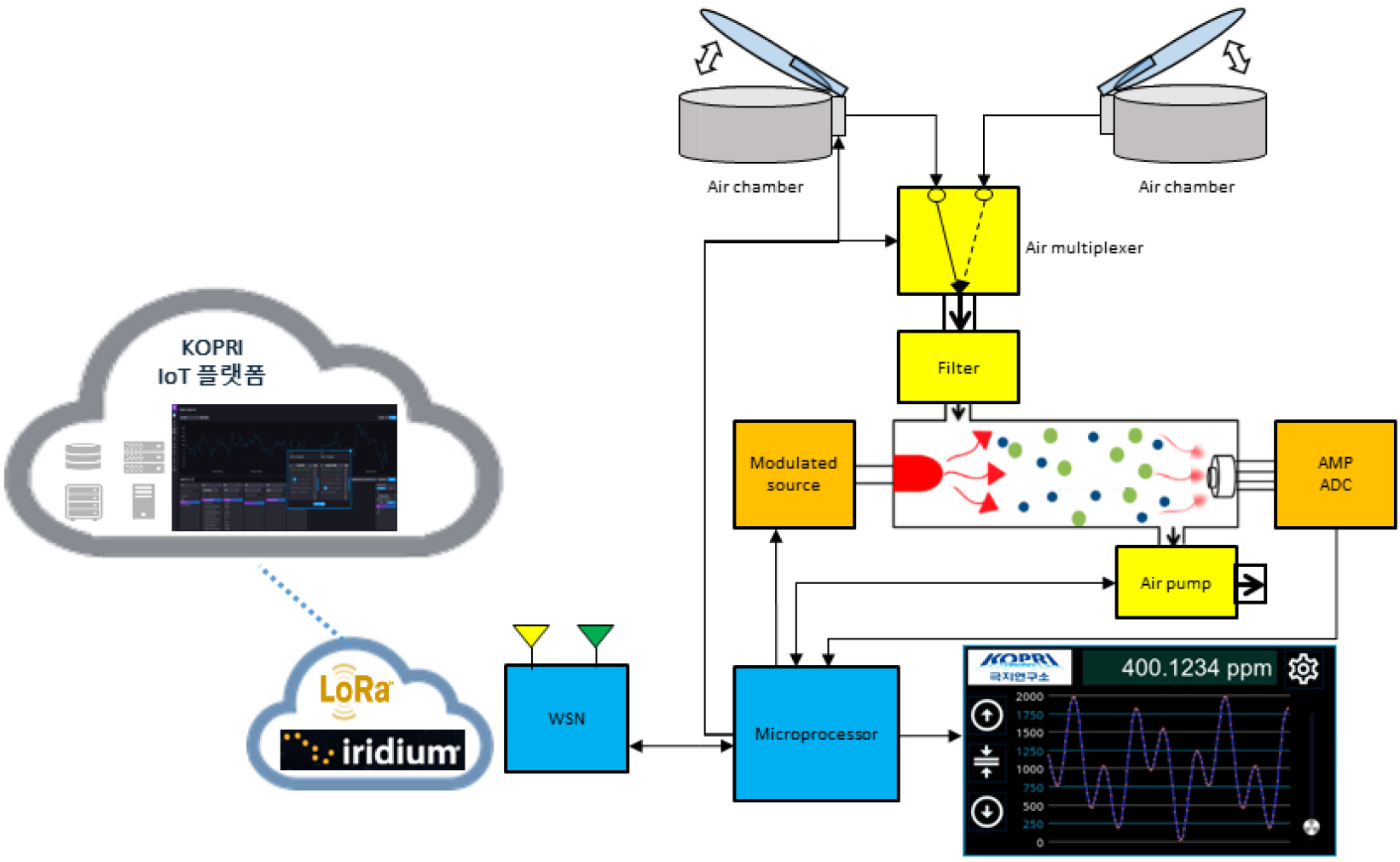
-
Development and Evaluation of a Ground CO2 Measurement System
이산화탄소(CO2) 측정 시스템의 개발 및 적용성 평가
-
Keunbo Park
박근보
- Demand has increased for field-deployable, high-precision instruments to quantify CO2 exchange at the permafrost–atmosphere interface. To meet this need, we developed …
지구 평균 기온 상승은 산업화 이후 증가한 온실가스 배출과 밀접한 관련이 있으며, 특히 고위도 지역의 영구동토층 해빙은 저장된 유기탄소의 대기 방출을 통해 …
- Demand has increased for field-deployable, high-precision instruments to quantify CO2 exchange at the permafrost–atmosphere interface. To meet this need, we developed a CO2 analyzer based on non-dispersive infrared (NDIR) spectroscopy integrated with an MCU-based controller, a real-time compensation algorithm, a communication module, and a GUI-based visualization system to ensure stable field operation. The system incorporates zero and span calibrations with standard gases, moving-average and adaptive signal filtering, anomaly detection, and continuous data logging to improve robustness. Performance was evaluated using CO2 standards at 0.600 ppm, 429.86 ppm, and 953.55 ppm; metrics assessed included accuracy, precision, response time, linearity, and zero stability. Experimental results show close agreement with reference concentrations across the tested range and performance comparable to a commercial high-precision system (LI-COR LI-7810), including accuracy within ±1%, precision better than 0.560, and minimal long-term zero drift. A 1:1 comparison confirmed excellent linearity and high correlation between the instruments.
- COLLAPSE
지구 평균 기온 상승은 산업화 이후 증가한 온실가스 배출과 밀접한 관련이 있으며, 특히 고위도 지역의 영구동토층 해빙은 저장된 유기탄소의 대기 방출을 통해 지구가열화를 가속할 잠재성이 크다. 이에 따라 동토–대기 경계면에서 발생하는 CO2 교환 특성을 정량적으로 규명하기 위한 정밀 현장 관측 기술의 필요성이 증대되고 있다. 본 연구에서는 이러한 과학적·정책적 요구에 대응하여 비분산적외선(NDIR) 분광 원리를 기반으로 한 정밀 CO2 측정시스템을 설계·제작하였다. 측정 시스템은 MCU 기반 제어기, 실시간 보정 알고리즘, 통신 모듈 및 GUI 기반 시각화 시스템을 통합하여 안정적으로 운용 가능하도록 구현하였다. 개발된 측정 시스템은 표준가스를 이용한 영점 및 스팬 교정 기능을 포함하며, 이동평균 및 적응형 필터 기반 신호 처리, 비정상 신호 제거 알고리즘, 실시간 데이터 로깅 기능을 적용하였다. 성능 검증은 0.600 ppm, 429.860 ppm, 953.550 ppm의 CO2 표준가스를 이용해 정확도, 정밀도, 응답시간, 선형성 및 영점 안정성을 평가하는 방식으로 수행하였다. 실험 결과, 모든 농도 구간에서 측정값은 표준가스 농도와 일치하는 수준을 유지하였으며, 정확도 ±1% 이내, 정밀도 0.560 이하, 장기 영점 드리프트를 포함하여 상용되고 있는 정밀 측정 시스템(LI-COR LI-7810)와 동등한 성능을 확보하였다. 또한 1:1 비교 분석에서 두 장비의 측정값은 높은 상관성을 보이며 우수한 선형성을 나타냈다.
-
Development and Evaluation of a Ground CO2 Measurement System
Journal Informaiton
 Journal of the Korean Geotechnical Society
Journal of the Korean Geotechnical Society
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Journal of the Korean Geotechnical Society
Journal of the Korean Geotechnical Society











