-

-
Engineering Characteristics of CLSM with a Cement, Fly Ash, and Plaster Mixing Ratio
시멘트, 플라이애쉬, 석회 배합비율에 따른 유동성 채움재의 공학적 특성 연구
-
Young-Tae Seo, Min-Ji Jung, Byeong-Jun Kim
서영태, 정민지, 김병준
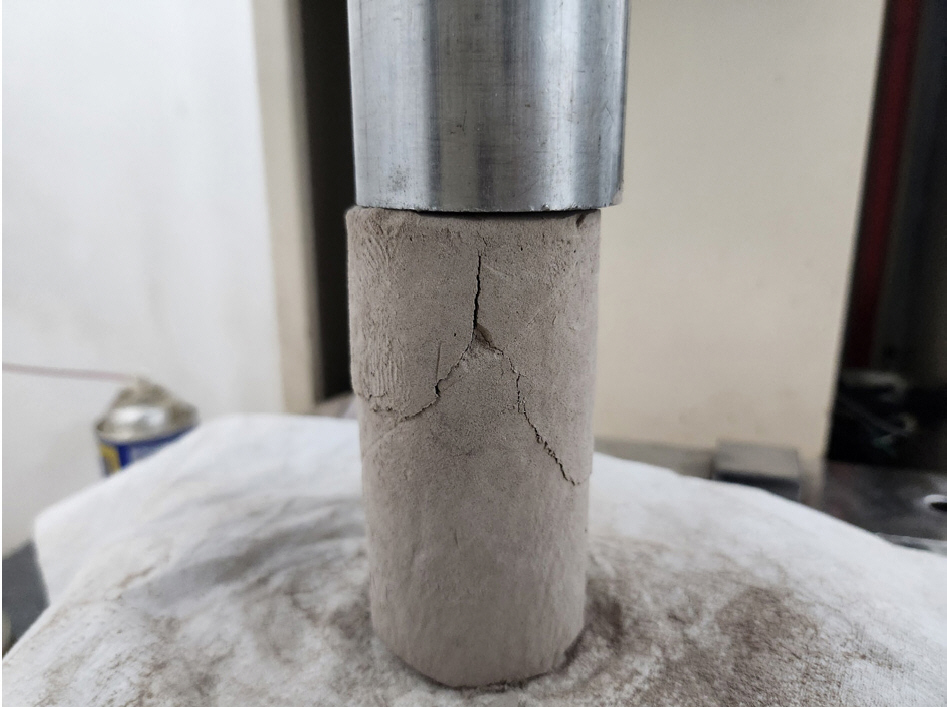
- In this study, we propose a standard for the uniaxial compressive strength of controlled low-strength material (CLSM) with a mixing ratio of …
본 연구에서는 도로 하부 공동에 사용되는 유동성 채움재의 일축압축강도 기준을 제안하고자 한다. 국토교통부에 따르면 보조기층과 노상층은 양생 10일 기준 압축강도 2.0MPa 이상으로 …
- In this study, we propose a standard for the uniaxial compressive strength of controlled low-strength material (CLSM) with a mixing ratio of cement, fly ash, and plaster. According to the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport, the uniaxial compressive strength of the auxiliary base layer or road surface layer should be 2.0 MPa at 10 days of curing. However, the uniaxial compressive strength of CLSM currently used in Busan Metropolitan City is below 0.6 MPa. Herein, fly ash, cement, and plaster were mixed to prepare a test material and uniaxial compressive strength tests were conducted after curing for 7, 14, and 28 days. The uniaxial compressive strengths of the cement-based test bodies rarely exceeded 1.0 MPa; only two samples achieved compressive strengths of 1.0 MPa or higher. After applying 5%–10% of plaster, the long-term compressive strength was typically improved to 1.0 MPa or higher at 28 days of curing and reached up to 1.879 MPa at maximum.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구에서는 도로 하부 공동에 사용되는 유동성 채움재의 일축압축강도 기준을 제안하고자 한다. 국토교통부에 따르면 보조기층과 노상층은 양생 10일 기준 압축강도 2.0MPa 이상으로 제안하고 있다. 하지만 현재 부산광역시에서 사용하는 유동성 채움재의 일축압축강도는 0.6MPa 이하로 국토교통부가 제안한 압축강도 대비 낮은 일축압축강도를 나타냈다. 본 연구에서는 플라이애시와 시멘트, 석회를 배합하여 공시채를 제작하였으며, 7일, 14일, 28일 기준으로 각각 양생 후 일축압축강도 시험을 수행하였다. 시험 결과 플라이애시, 시멘트를 사용한 공시채의 일축압축강도는 대부분 1.0MPa을 넘지 못하며, 1.0MPa 이상의 압축강도를 나타낸 시료는 단 2회에 뿐이었다. 반면 석회를 5~10% 적용한 경우 장기 압축강도가 양생 28일 기준 대부분 1.0MPa 이상 나타났으며, 최대 1.879MPa까지 나타났다.
-
Engineering Characteristics of CLSM with a Cement, Fly Ash, and Plaster Mixing Ratio
-
-
A Study on the Application of an AI Model for Joint Detection using NM-GPR
NM-GPR을 활용한 공동 탐지 AI 모델 적용성 연구
-
Gi-Seok Lee, Jin-Wook Oh, Kang-Ile Lee
이기석, 오진욱, 이강일
- This study examines the characteristics of noise-modulated ground penetrating radar (NM-GPR), a device used in GPR-based cavity detection to prevent ground subsidence. …
본 연구는 지반 침하 예방을 위해 수행되는 GPR(Ground Penetrating Radar) 공동 탐사에 활용되는 장비 중 NM-GPR(Noise-modulated GPR)의 특성을 분석하고, 이를 기반으로 공동 …
- This study examines the characteristics of noise-modulated ground penetrating radar (NM-GPR), a device used in GPR-based cavity detection to prevent ground subsidence. It develops an AI-based cavity detection model tailored to its unique features. NM-GPR enhances data visibility through noise modulation, reducing power consumption and enabling rapid and efficient road surveys. Despite its technological advancement, AI-based detection methods for NM-GPR remain underdeveloped. To address this gap, we compare NM-GPR with conventional impulse-based GPR systems and develop an AI model optimized for the distinct characteristics of the NM-GPR. During model development, we applied data preprocessing and augmentation techniques to analyze their impact on detection outcomes and constructed a dedicated training dataset. Using this dataset, we implemented You Only Look Once (YOLO) and faster R-CNN models, evaluating their performance based on mean average precision (mAP), precision, and recall. Finally, we applied the trained models to a test dataset to assess their feasibility for real-world application.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 지반 침하 예방을 위해 수행되는 GPR(Ground Penetrating Radar) 공동 탐사에 활용되는 장비 중 NM-GPR(Noise-modulated GPR)의 특성을 분석하고, 이를 기반으로 공동 탐지 모델을 개발하여 적용하는 연구를 수행하였다. NM-GPR은 노이즈를 활용하여 데이터의 시인성을 높이고, 사용 전력을 절감하여 빠른 속도로 도로에서 탐사할 수 있는 장점을 갖고 있다. 그러나 최신 기술임에도 불구하고, 인공지능 기반 탐지 기술의 개발은 미흡한 실정이다. 따라서 본 연구에서는 임펄스 신호를 사용하는 기존 GPR 장비와 NM-GPR을 비교 분석하고, NM-GPR 장비의 특성에 적합한 AI 모델을 적용성을 평가 하였다. AI 모델 적용성 평가를 위해 기존의 데이터 전처리 및 증강 기법을 적용하여 탐지 결과의 변화를 분석하고, 학습 데이터셋을 구축하였다. 구축된 학습 데이터셋을 활용하여 YOLO(You Only Look Once)와 Faster R-CNN 모델을 적용한 후, mAP(mean Average Precision), 정밀도(Precision), 재현율(Recall)을 분석하였다. 또한, 시험 데이터셋을 활용하여 모델의 현장 적용 가능성을 평가하였다.
-
A Study on the Application of an AI Model for Joint Detection using NM-GPR
-
-
Development of an MS–ANN Model for Predicting Ground Subsidence and Supporting Reinforcement Decision-Making in Abandoned Mine Areas
MS-ANN을 활용한 국내 폐광산 지반침하 예측 및 보강 의사결정 모델 개발
-
Min-Koan Kim
김민관
- Ground subsidence in abandoned mines is a critical geohazard that threatens infrastructure stability in Korea, necessitating accurate prediction and efficient reinforcement strategies. …
국내 폐광산의 지반침하는 건축물 및 인프라 안정성을 위협하는 주요 지질재해로, 정확한 예측과 효율적인 보강 전략이 요구된다. 본 연구는 국내 폐광산의 지반침하 예측과 …
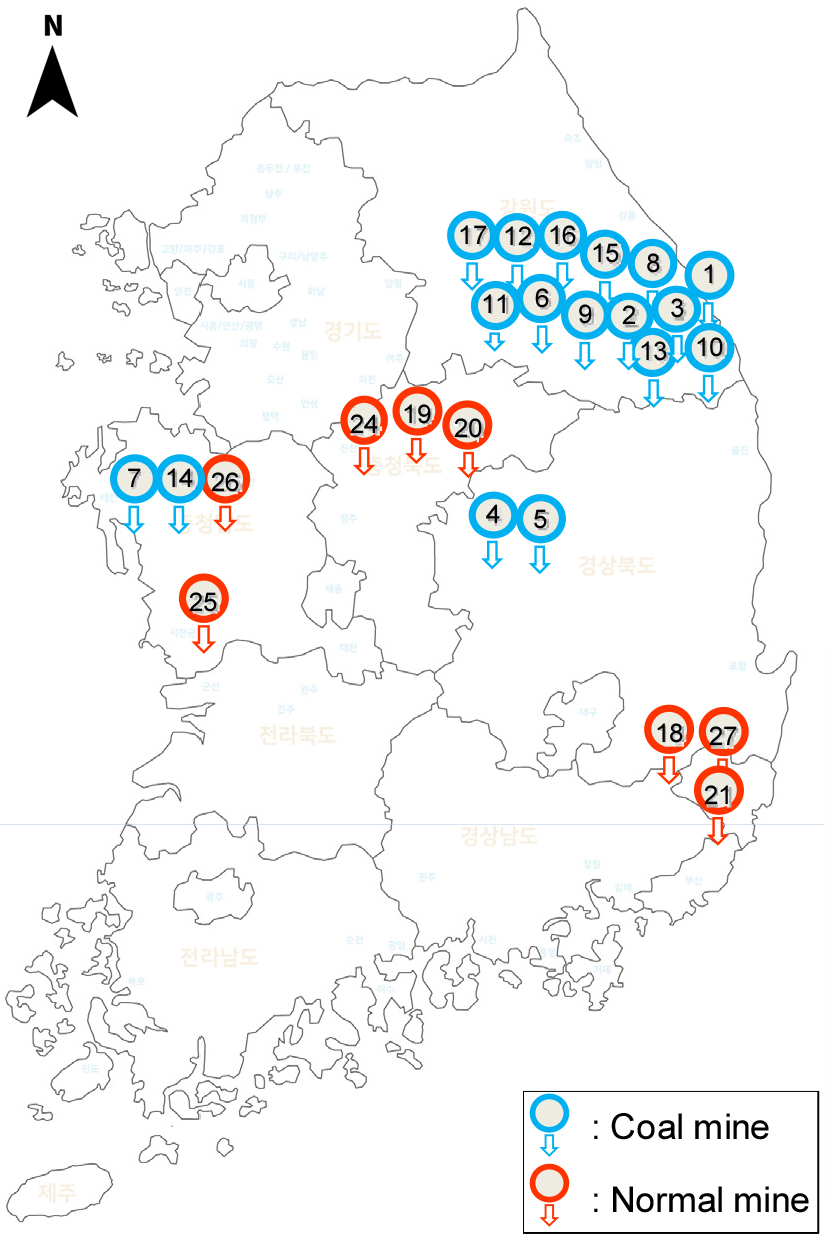
- Ground subsidence in abandoned mines is a critical geohazard that threatens infrastructure stability in Korea, necessitating accurate prediction and efficient reinforcement strategies. This study developed the Mine Subsidence– Artificial Neural Network (MS–ANN) model to predict ground subsidence and recommend reinforcement methods for abandoned mines in Korea. Using 247 subsidence cases from the Korean Mine Reclamation Corporation and 30 influencing factors, including geological, mining, and land-use data, the MS–ANN was designed with a feedforward neural network architecture optimized using the resilient backpropagation algorithm. The model comprises 21 input nodes, 2 hidden layers (with 21 and 28 nodes), and 9 output nodes to predict subsidence occurrence, extent, and reinforcement methods. Training on 229 cases yielded correlation coefficients of 0.968–0.9946 and an average inference error rate (AIER) of 4.5%–7.0%. However, validation on 18 test cases recorded correlation coefficients of 0.9855–0.9961 and an AIER of 2.5%–3.5%. The MS–ANN demonstrates stable prediction performance across various mine types, aiding subsidence risk assessment, reinforcement method recommendations, and sustainable land use. It is expected to enhance the cost-efficiency of mine reclamation by mitigating risks and costs associated with geohazards in Korea.
- COLLAPSE
국내 폐광산의 지반침하는 건축물 및 인프라 안정성을 위협하는 주요 지질재해로, 정확한 예측과 효율적인 보강 전략이 요구된다. 본 연구는 국내 폐광산의 지반침하 예측과 보강 공법 결정을 위해 Mine Subsidence-Artificial Neural Network(MS-ANN) 모델을 개발하였다. 한국광해광업공단의 247개 침하 사례와 30개 영향인자(지질, 채굴, 토지이용 데이터 등)를 활용하여 피드포워드 신경망(FNN) 구조를 기반으로 모델을 설계하였다. MS-ANN은 RPROP(Resilient Backpropagation) 알고리즘으로 최적화되었다. 이 모델은 입력층 21개 노드, 두 개의 은닉층(각각 21개 및 28개 노드), 출력층 9개 노드로 구성되어 지반침하 발생, 범위, 보강 공법을 예측한다. 229개 학습 데이터로 훈련한 결과, 예측 정확도(R2) 0.968~0.9946, 평균 추론 오차율(AIER) 4.5~7.0%를 달성하였으며, 시험 데이터(18개) 검증에서 R2 0.9855~0.9961, AIER 2.5~3.5%를 기록하였다. MS-ANN은 다양한 광산 유형에서 안정적인 예측 성능을 보이며, 침하 위험 평가, 보강 공법 추천, 그리고 지속가능한 토지 이용을 지원한다. 본 모델은 폐광산 복구 사업의 비용 효과성을 높이고, 지질재해로 인한 위험을 최소화하는 데 기여할 것으로 기대된다.
-
Development of an MS–ANN Model for Predicting Ground Subsidence and Supporting Reinforcement Decision-Making in Abandoned Mine Areas
-
-
Assessment of Ground Subsidence along Daesin Road in the Sangpyeong Industrial Complex Using Gravity Field Interpretation and 3-D Density Modeling
중력장 해석과 3-D 밀도 모델링을 통한 상평산단 대신로의 지반침하 진단
-
Sungchan Choi, Sung-Wook Kim, Dae-Hong Go, Yeong-Jae Lee, Sung-Min Bae, Gichun Kang
최승찬, 김성욱, 고대홍, 이영재, 배성민, 강기천
- This study investigates the causes of recurrent ground subsidence along Daesin Road in the Sangpyeong Industrial Complex, Jinju, Korea, using gravity field …
이 연구는 경상남도 진주시 상평산단 대신로에서 반복적으로 발생한 지반침하의 원인과 지하 구조를 분석하기 위해 중력장 해석과 3차원 밀도 모델링을 중심으로 수행되었다. 상평산단 …
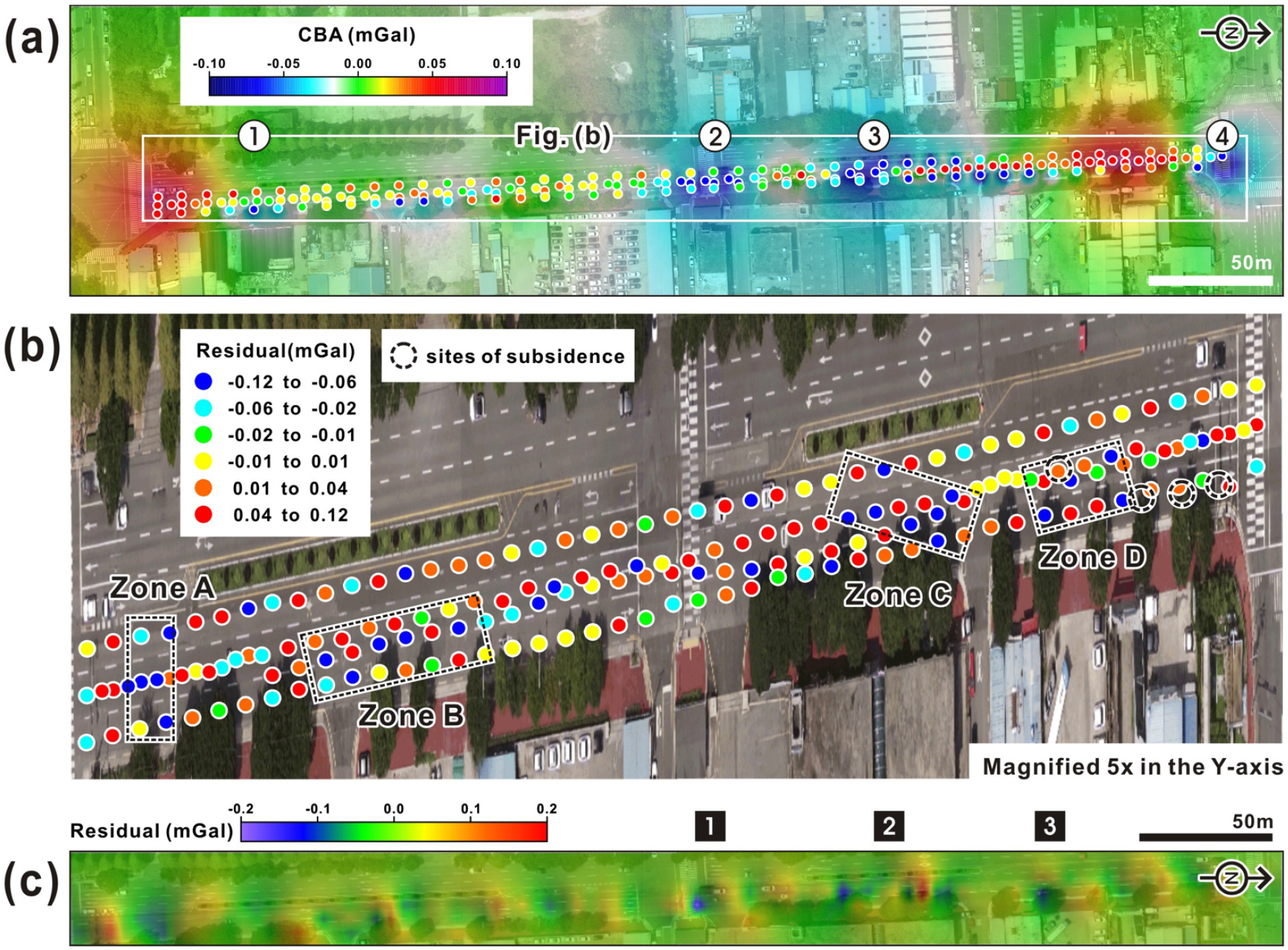
- This study investigates the causes of recurrent ground subsidence along Daesin Road in the Sangpyeong Industrial Complex, Jinju, Korea, using gravity field interpretation and three-dimensional (3D) density modeling. The area, a former floodplain, is geologically vulnerable owing to loosely consolidated clayey sediments and heterogeneous stratification, which, combined with rainfall and groundwater fluctuations, increase subsidence risk. Ground irregularities, attenuated ground-penetrating radar signals, and isolated low-gravity anomalies reveal low-density zones (LDZs) beneath the surface. Notably, the LDZs identified through 3D modeling align with the location of buried abandoned pipelines, indicating a man-made influence on subsidence. Integrating geological, hydrogeological, and geophysical datasets enhances understanding of urban subsidence mechanisms. The proposed methodology offers an effective framework for hazard assessment and early warning systems in geologically vulnerable urban areas.
- COLLAPSE
이 연구는 경상남도 진주시 상평산단 대신로에서 반복적으로 발생한 지반침하의 원인과 지하 구조를 분석하기 위해 중력장 해석과 3차원 밀도 모델링을 중심으로 수행되었다. 상평산단 지역은 과거 하천 매립지로 지질학적 취약성과 미고결 점성토의 불균질한 분포 특성을 보이며, 강우 및 지하수위 변동과 결합되어 침하 위험이 증가하는 것으로 나타났다. 지표면의 불규칙한 기복, GPR 탐사에서의 반사 신호 감쇠, 그리고 중력장 해석에서 나타난 고립된 저중력이상대는 하부 지반 내 저밀도층의 존재를 시사한다. 특히, 3차원 밀도 모델링 결과, 저밀도층은 폐관로 하부와 밀접하게 지반침하의 인위적 기여 가능성을 높인다. 연구에 이용한 지질·수문·지구물리자료의 통합 해석으로 도시형 지반침하의 메커니즘을 규명하며, 향후 침하 예측 및 사전 경보체계 구축을 위한 실효성 있는 분석방법을 제시한다.
-
Assessment of Ground Subsidence along Daesin Road in the Sangpyeong Industrial Complex Using Gravity Field Interpretation and 3-D Density Modeling
-
-
Analysis of Asymmetric Load Behavior in Load-Distribution Anchors
하중분산형 앵커의 편하중 거동특성 분석
-
Yong-Jae Song, Kang-Il Lee, Chi-young Yang
송용재, 이강일, 양치영
- A known issue with load-distributing anchors is the occurrence of asymmetric loading, resulting from differences in the lengths of individual strands connected …
하중분산형 앵커에서 발생하는 편하중은 내하체에 연결된 각 강연선의 길이 차이로 인해 발생된다는 문제점이 있다. 하중분산형 앵커에서 발생하는 편하중 거동을 정량적으로 분석하기 위해 …
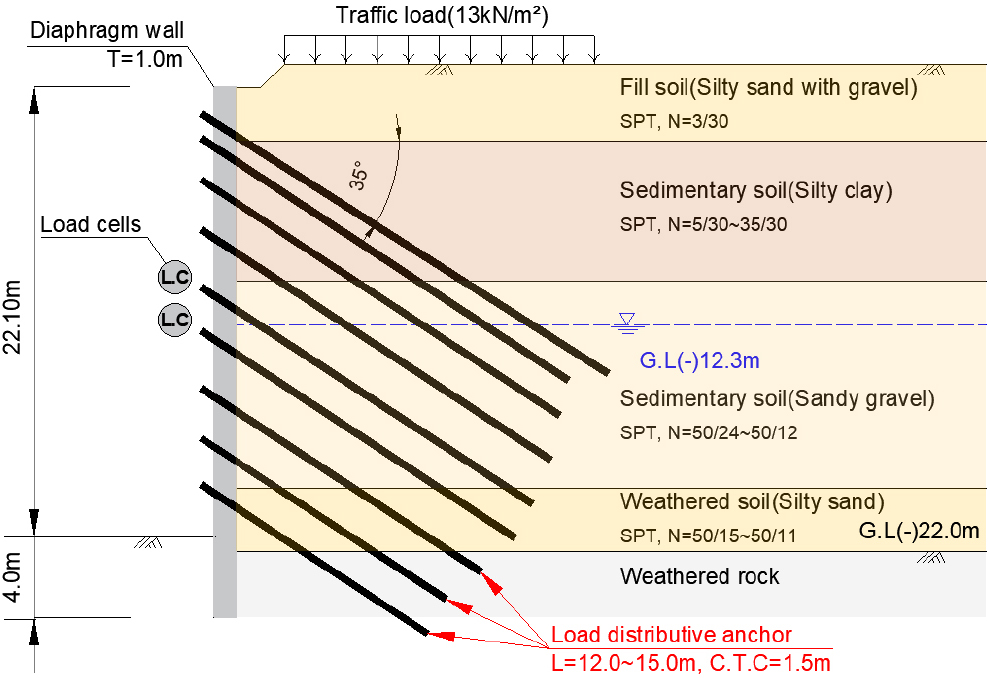
- A known issue with load-distributing anchors is the occurrence of asymmetric loading, resulting from differences in the lengths of individual strands connected to the anchor body. To quantitatively analyze the behavior of asymmetric loads in such anchors, the loads on each strand were measured using mono-cells, and the results served as the basis for analysis. The measurements revealed that when asymmetric loading occurs simultaneously in both the anchor body and the strands, the asymmetric load can account for up to approximately 76% of the total load. This finding indicates that even if the total load applied to the anchor does not reach the design limit, localized failure may still occur in strands subjected to concentrated asymmetric loading.
- COLLAPSE
하중분산형 앵커에서 발생하는 편하중은 내하체에 연결된 각 강연선의 길이 차이로 인해 발생된다는 문제점이 있다. 하중분산형 앵커에서 발생하는 편하중 거동을 정량적으로 분석하기 위해 내하체와 연결된 각 강연선에 작용하는 하중을 모노셀을 통해 계측하고, 이를 기반으로 분석을 수행하였다. 계측 결과 내하체 및 강연선간에 편하중이 동시에 발생할 경우, 최대 76% 수준의 편하중이 발생하는 것으로 나타났다. 이는 앵커에 작용하는 전체 하중이 설계 한계에 도달하지 않더라도, 편하중이 집중된 강연선에서 국부적으로 파단이 발생할 수 있음을 보여주고 있다.
-
Analysis of Asymmetric Load Behavior in Load-Distribution Anchors
Journal Informaiton
 Journal of the Korean Geotechnical Society
Journal of the Korean Geotechnical Society
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Journal of the Korean Geotechnical Society
Journal of the Korean Geotechnical Society











